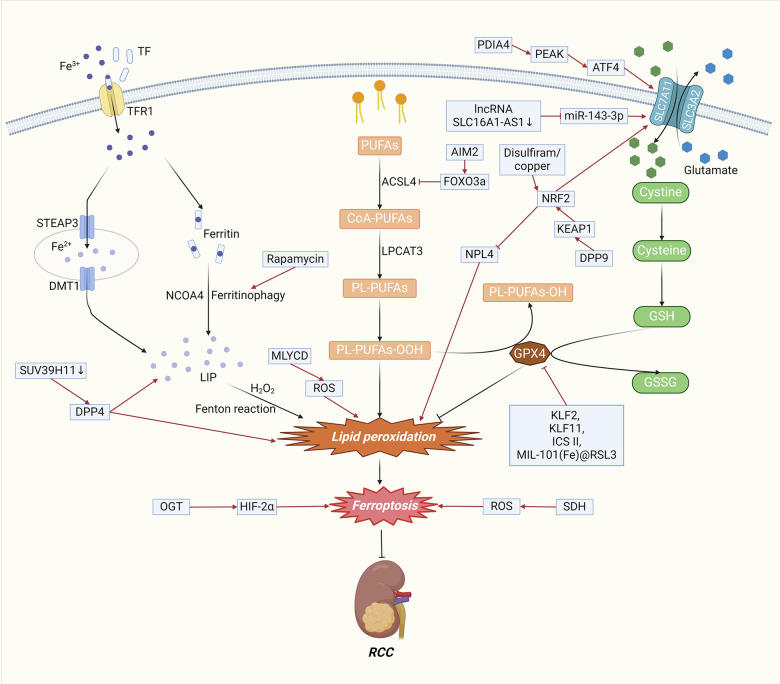
Fig. 2. The molecular mechanism of ferroptosis in RCC.
The modulation of ferroptosis can exert significant effects on RCC through various mechanisms, encompassing the regulation of GSH levels, lipid metabolism, iron metabolism, the NRF2 signaling pathway, the HIF-2α signaling pathway, and the ROS signaling pathway. Abbreviations: PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; CoA, coenzyme A; PL-PUFAs, phospholipid-containing PUFAs; ACSL4, acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; TF, transferrin; TFR1, transferrin receptor 1; STEAP3, iron oxide reductase steam 3; DMT1, divalent metal transporter 1; NCOA4, nuclear receptor coactivator 4; LIP, labile iron pool; SLC7A11, solute carrier family 7 member 11; SLC3A2, solute carrier family 3 member 2; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, Oxidized glutathione; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; KLF, Kruppel-like factor; ICS II, Icariside II; DPP4, dipeptidyl-peptidase-4; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; OGT, O-GlcNAc transferase; HIF-2α, hypoxia-inducible factor-2α; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase; ROS, Reactive Oxygen Species.