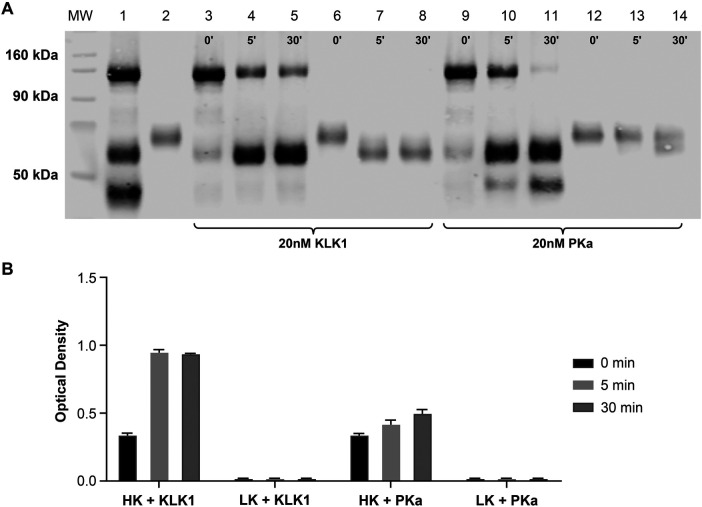
Figure 3.
Comparative kininogen digestion by tissue vs. plasma kallikrein. Purified HK and LK were analyzed by western blotting (A) or an ELISA (B) using M4-B4 as a capture antibody and 11H05 and 13B12 as detection antibodies following incubation with either KLK1 or PKa. The western blot analysis was performed using a polyclonal sheep anti-kininogen antibody for detection that cross-reacted with LK as well as HK. The lane compositions are as follows: molecular-weight markers (MW), a mixture of purified intact HK and HKa (1.5 µM each) (lane 1); purified LK (1.5 µM) (lane 2); HK (1.5 µM) incubated with 20 nM KLK1 for 0, 5, and 30 min (lanes 3–5); LK (1.5 µM) incubated with 20 nM KLK1 for 0, 5, and 30 min (lanes 6–8); HK (1.5 µM) incubated with 20 nM PKa for 0, 5, and 30 min (lanes 9–11); and LK (1.5 µM) incubated with 20 nM PKa for 0, 5, and 30 min (lanes 12–14). HK, high-molecular-weight kininogen; HKa, cleaved high-molecular-weight kininogen; KLK1, tissue kallikrein 1; LK, low-molecular-weight kininogen; MW, molecular weight; PK, prekallikrein; PKa, plasma kallikrein.