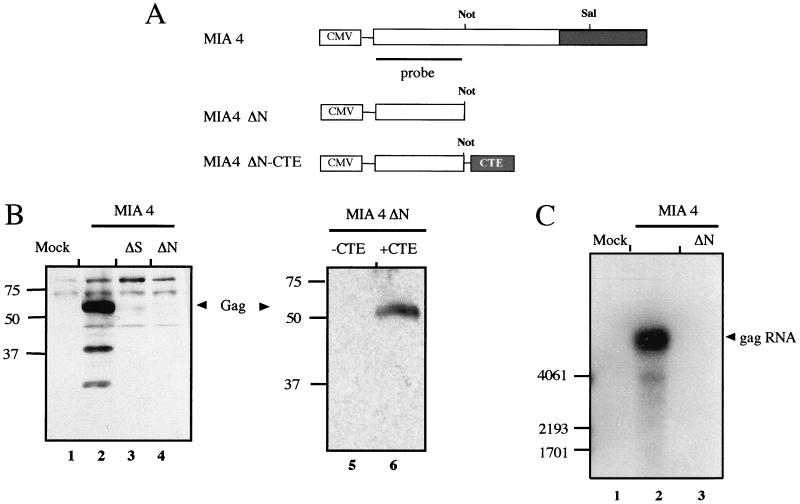
FIG. 2.
Analysis of IAP Gag expression. (A) Schematic diagram of plasmid pL-MIA4 encoding the gag and pol open reading frames of MIA14 (57) and plasmids 3-MIA4ΔN without and 3-MIA4ΔN-CTE with CTE. The relative positions of the restriction sites used for the deletion constructs pL-MIA4ΔS and pL-MIA4ΔN, as well as the positions of the RNA elements, are indicated. (B) Immunoblot analysis of Cos-7 cells transiently transfected with plasmids pL-MIA4, pL-MIA4ΔS, and pL-MIA4ΔN (lanes 2, 3, and 4) or mock transfected (lane 1) (left blot) and with plasmids 3-MIA4ΔN (lane 5)and 3-MIA4ΔN-CTE (lane 6) (right blot). The cell lysates were analyzed with a polyclonal rabbit anti-IAP Gag serum, and the IAP Gag polyprotein is marked with arrowheads. The additional proteins migrating with higher mobility than the Gag polyprotein correspond to Gag cleavage products (lane 2) (57). (C) Northern blot analysis of Cos cells mock transfected (lane 1) or transfected with pL-MIA4 or pL-MIA4ΔN (lanes 2 and 3). Total RNA was subjected to Northern blot analysis, and IAP Gag-specific RNA was detected with a 32P-labeled probe directed against the gag coding region, as depicted in panel A. The gag RNA is indicated on the right, and RNA standards (in nucleotides) are given on the left.