Abstract
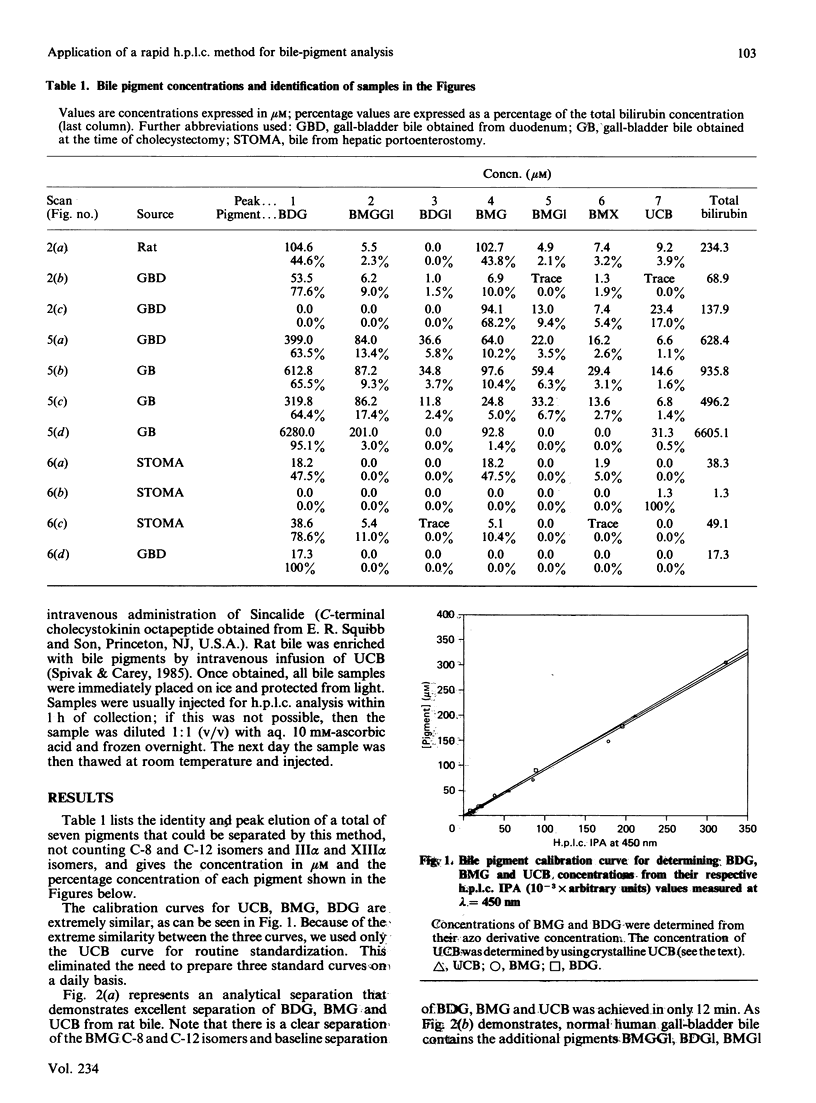
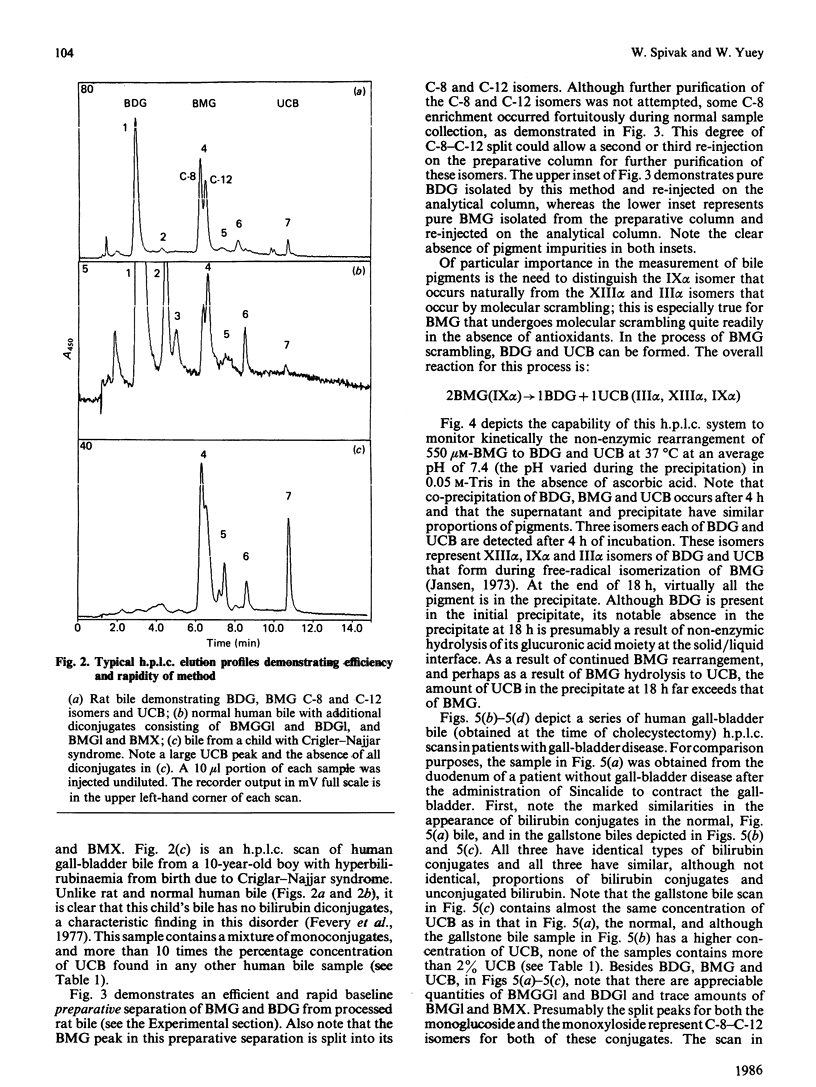
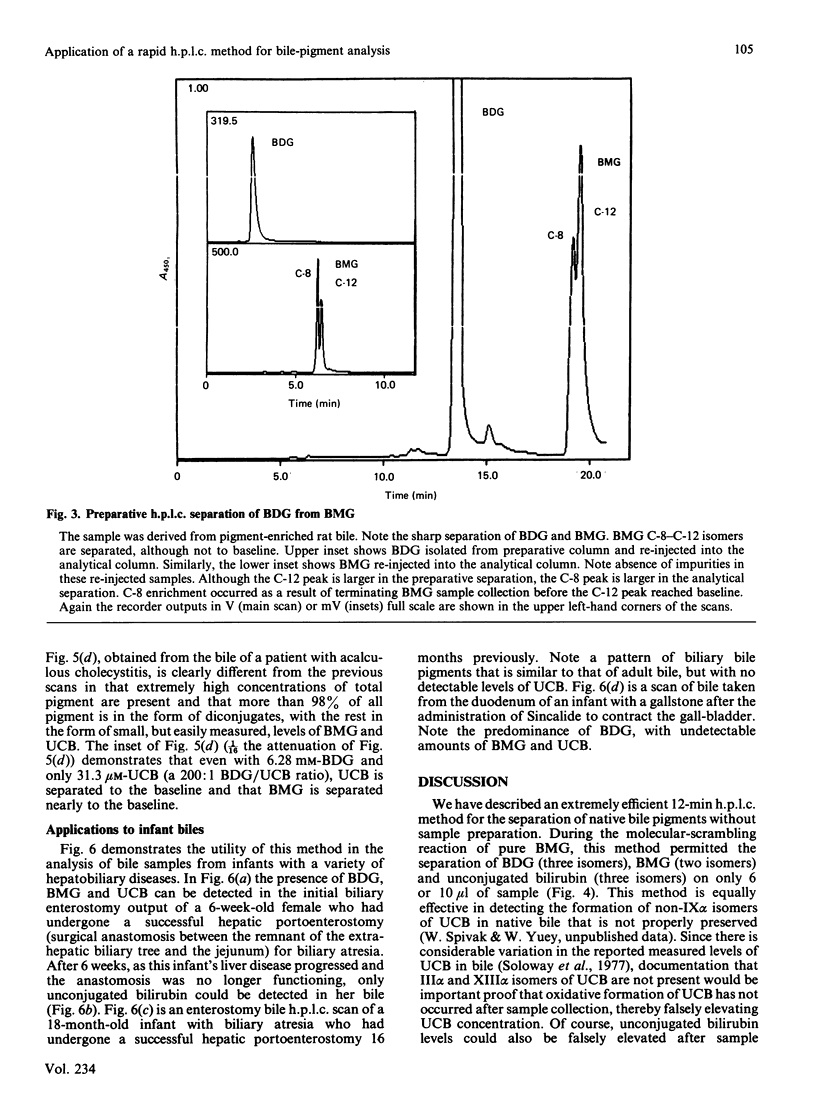
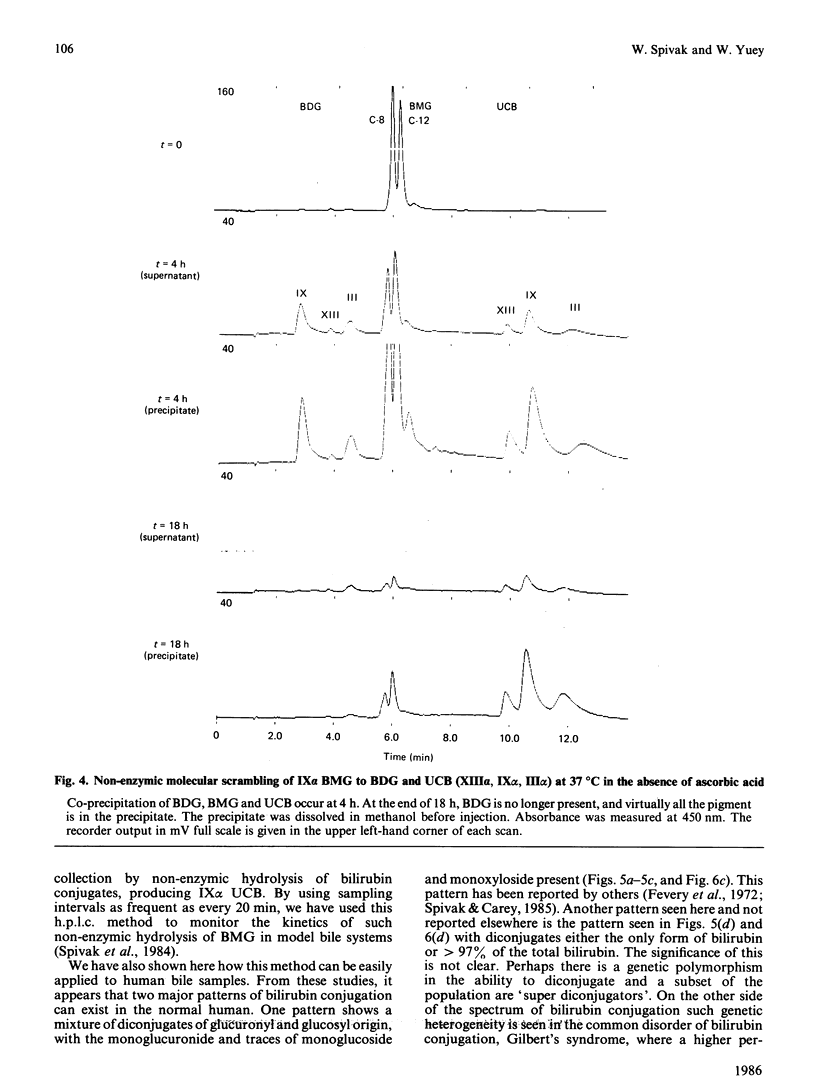
We have developed an extremely rapid and efficient reverse-phase h.p.l.c. method for the measurement of bilirubin and its conjugates in human bile and in model bile systems. Our method involves the use of a Perkin-Elmer 3 mu C18 column and a methanol/sodium acetate/aq. ammonium acetate buffer system. Three isomers of bilirubin diglucuronide (BDG), two isomers of bilirubin monoglucuronide (BMG), three isomers of unconjugated bilirubin (UCB) and minor conjugates containing glucose and xylose were separated in 12 min. Initial quantification of BDG and BMG was based on the use of the ethyl anthranilate azo derivative of bilirubin (AZO UCB); however, the standard curves for BDG, BMG and UCB were similar enough to permit quantification to be later based on the UCB standard curve only, thereby simplifying the quantification process. Routine direct injection of 6 or 10 microliter of crude undiluted or diluted (1:1) bile sample was sufficient for analysis. The method was helpful in diagnosing biliary-tract obstruction in a newborn and a partial deficiency state of bilirubin conjugation (Crigler-Najjar syndrome) in a 10-year-old male. When the method was applied to biles of patients both with and without gallstones, levels of UCB were less than 2% of total pigment, consistent with previous reports. Because of its speed and efficiency, this method has the potential for a broad range of applications including enzymic, kinetic and bile sample analyses.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON R., HUESTIS R. R., MOTULSKY A. G. Hereditary spherocytosis in the deer mouse. Its similarity to the human disease. Blood. 1960 Apr;15:491–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanckaert N., Compernolle F., Leroy P., Van Houtte R., Fevery J., Heirwegh K. P. The fate of bilirubin-IXalpha glucuronide in cholestasis and during storage in vitro. Intramolecular rearrangement to positional isomers of glucuronic acid. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 1;171(1):203–214. doi: 10.1042/bj1710203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonyapisit S. T., Trotman B. W., Ostrow J. D. Unconjugated bilirubin, and the hydrolysis of conjugated bilirubin, in gallbladder bile of patients with cholelithiasis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jan;74(1):70–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury J. R., Chowdhury N. R., Gärtner U., Wolkoff A. W., Arias I. M. Bilirubin diglucuronide formation in intact rats and in isolated Gunn rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):595–603. doi: 10.1172/JCI110486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelius C. E., Kelley K. C., Himes J. A. Heterogeneity of bilirubin conjugates in several animal species. Cornell Vet. 1975 Jan;65(1):90–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvaldestin P., Mahu J. L., Metreau J. M., Arondel J., Preaux A. M., Berthelot P. Possible role of a defect in hepatic bilirubin glucuronidation in the initiation of cholesterol gallstones. Gut. 1980 Aug;21(8):650–655. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.8.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevery J., Blanckaert N., Heirwegh K. P., Préaux A. M., Berthelot P. Unconjugated bilirubin and an increased proportion of bilirubin monoconjugates in the bile of patients with Gilbert's syndrome and Crigler-Najjar disease. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):970–979. doi: 10.1172/JCI108877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevery J., Van Damme B., Michiels R., De Groote J., Heirwegh K. P. Bilirubin conjugates in bile of man and rat in the normal state and in liver disease. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2482–2492. doi: 10.1172/JCI107062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollan J. L., Huang S. N., Billing B., Sherlock S. Prolonged survival in three brothers with severe type 2 Crigler-Najjar syndrome. Ultrastructural and metabolic studies. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jun;68(6):1543–1555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon E. R., Goresky C. A. A rapid and quantitative high performance liquid chromatographic method for assaying bilirubin and its conjugates in bile. Can J Biochem. 1982 Nov;60(11):1050–1057. doi: 10.1139/o82-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon E. R., Shaffer E. A., Sass-Kortsak A. Bilirubin secretion and conjujation in the Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II. Gastroenterology. 1976 May;70(5 PT1):761–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen P. L. The isomerisation of bilirubin monoglucuronide. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Dec 12;49(2):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda H., Nakayama F. Composition of bile pigment in gallstones and bile and their etiological significance. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Mar;93(3):353–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F., Assisi F. The ready isomerization of bilirubin IX- in aqueous solution. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(3):797–800. doi: 10.1042/bj1290797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Itoh S., Kawade N., Isobe K., Sugiyama S. An accurate and sensitive analysis by high-pressure liquid chromatography of conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin IX-alpha in various biological fluids. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 1;185(1):281–284. doi: 10.1042/bj1850281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt H. A., Lewinski M. A., Muller E. L., Porter-Fink V., DenBesten L. Ileal resection-induced gallstones: altered bilirubin or cholesterol metabolism? Surgery. 1984 Aug;96(2):154–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieg A., van Hees G. P., Heirwegh K. P. Uridine diphosphate-glucuronic acid-independent conversion of bilirubin monoglucuronides to diglucuronide in presence of plasma membranes from rat liver is nonenzymic. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):347–357. doi: 10.1172/JCI110458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloway R. D., Trotman B. W., Ostrow J. D. Pigment gallstones. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jan;72(1):167–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivak W., Carey M. C. Reverse-phase h.p.l.c. separation, quantification and preparation of bilirubin and its conjugates from native bile. Quantitative analysis of the intact tetrapyrroles based on h.p.l.c. of their ethyl anthranilate azo derivatives. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 1;225(3):787–805. doi: 10.1042/bj2250787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Linden W., Bergman F. Formation and dissolution of gallstones in experimental animals. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1977;17:173–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


