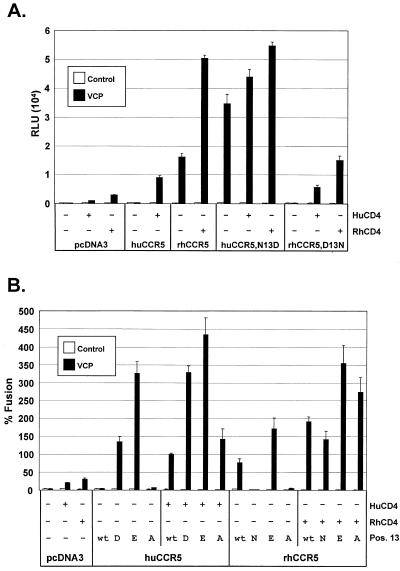
FIG. 2.
Human and rhesus CCR5 N-terminal mutations at position 13. (A) HIV-2/vcp was evaluated in cell-cell fusion on QT6 target cells expressing huCCR5, rhCCR5, or CCR5 mutants containing either an aspartic acid (D) or an asparagine (N) at position 13, as indicated. The ability of these CCR5 N-terminal mutants to support membrane fusion by VCP Env was assessed in the presence or absence of both human and rhesus CD4. Results are expressed as luciferase activity in relative light units (RLU). (B) VCP Env fusion was also assessed with CCR5 mutants containing either a glutamic acid (E) or an alanine (A) at position 13, as indicated. Values are represented as percent fusion, calculated using RLU normalized to VCP fusion on huCCR5 with huCD4. Mean values + SEM are represented.