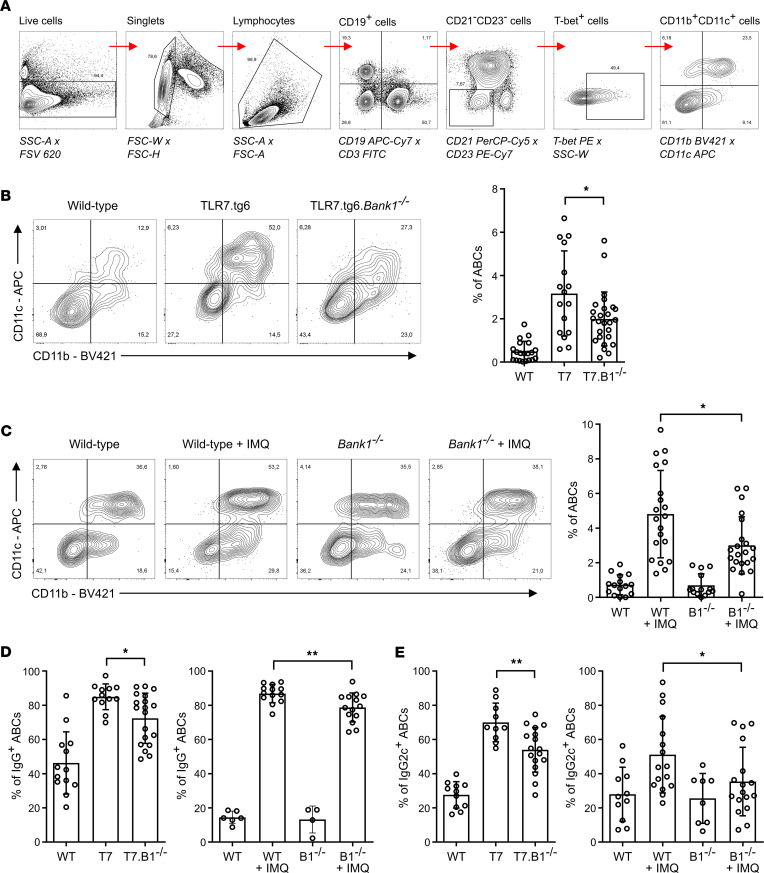
Figure 3. Age-associated B cells are reduced in the absence of Bank1 in TLR7.tg6 and IMQ-treated mice.
(A) Gating strategy to detect ABCs by flow cytometry. Sequential gating including: FSV620 live cells; FSC-W × FSC-H to gate single cells; SSC-A × FSC-A to gate lymphocytes; finally, ABCs were CD19+CD3–CD21–CD23–T-bet+CD11b+CD11c+ cells. (B) Frequency of ABCs among CD19+ B cells from the spleens of the TLR7.tg6 model. Total mice analyzed: WT (n = 20), T7 (n = 16), T7.B1–/– (n = 26). (C) Frequency of ABCs among CD19+ B cells from the spleens of the IMQ-induced model. Total mice analyzed: WT (n = 15), WT + IMQ (n = 20), B1–/– (n = 14), B1–/– + IMQ (n = 21). (D) Frequency of IgG+ cells among ABC population from the spleens of TLR7.tg6 and IMQ-induced models. Total mice analyzed: WT (n = 13), T7 (n = 12), T7.B1–/– (n = 19); and WT (n = 6), WT + IMQ (n = 13), B1–/– (n = 4), B1–/– + IMQ (n = 14). (E) Frequency of IgG2c+ cells among ABC population from the spleens of TLR7.tg6 and IMQ-induced models. Total mice analyzed: WT (n = 11), T7 (n = 10), T7.B1–/– (n = 17); and WT (n = 10), WT + IMQ (n = 16), B1–/– (n = 6), B1–/– + IMQ (n = 17). Each point represents 1 mouse. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Mann-Whitney U test with Welch’s correction was used to test statistical significance.