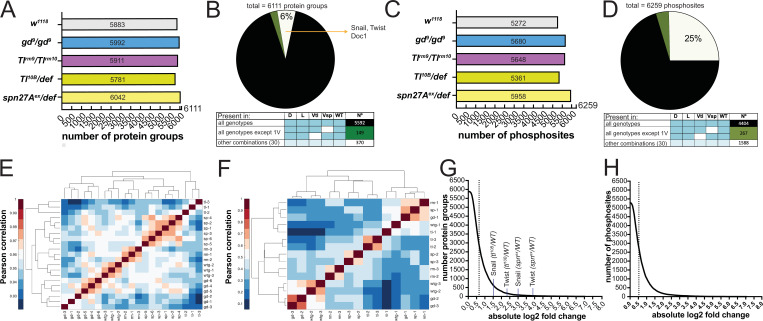
Figure 2. Proteomes and phosphoproteomes of wildtype and mutant embryos.
(A and C) Number of protein groups (A) or phosphosites (C) detected in wildtype, dorsalized (gd9), lateralized (Tlrm9/Tlrmrm10), and ventralized embryos (Toll10B/def and spn27Aex/def). (B and D) Intersection analysis of detected protein groups (B) or phosphosites (D). Black: detected in at least 1 replicate in all genotypes; green: detected in at least 1 replicate in all genotypes except 1 ventralized condition; white: detected in at least 1 replicate in any other combination. (E and F) Correlation matrix between the replicates of the proteomic (E) and phosphoproteomic (F) experiments using the Pearson correlation coefficient. Protein groups and phosphosites detected in all of the replicates in all of the genotypes were used to construct the correlation matrices. Proteomic (LFQ) analyses were performed using three technical replicates, with the exception of spn27aex/def and gd9 genotypes in which we used two biological replicates with three technical replicates each, making a total of six replicates for these two genotypes. For SILAC phosphoproteomic analyzes the protein lysate from embryos of each genotype was split in three and conducted three separate analyses. (G and H) Distribution of the number of protein groups (G) or phosphosites (H) exceeding an absolute fold change (vs. wild type, in log2 scale). Dotted line depicts the absolute fold change corresponding to 50% of the analyzed protein groups (G) or phosphosites (H).