Figure 1 |. Earliest preterm gut microbiota colonization in the NICU.
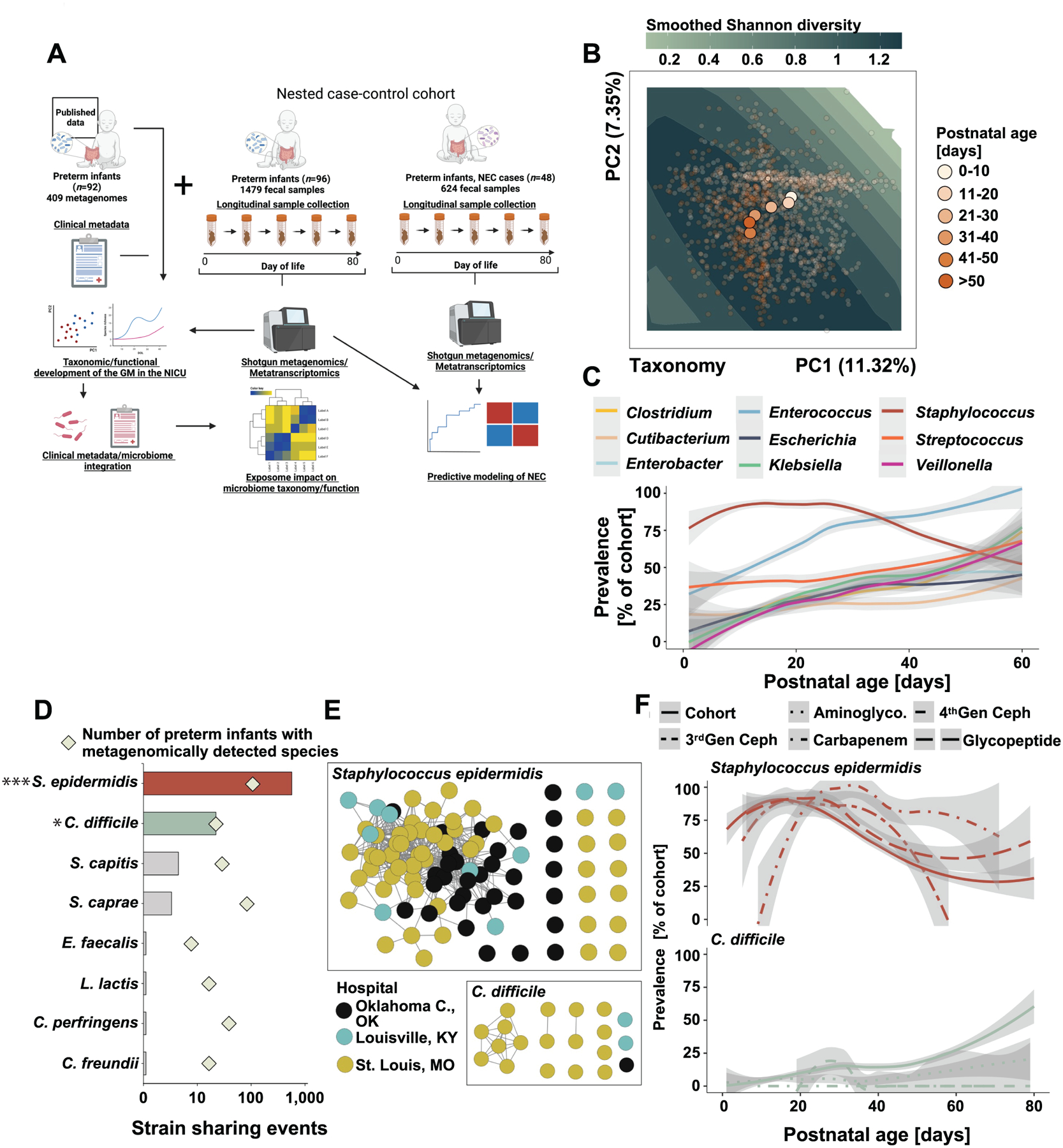
A) Schematic overview of the study design. Created with BioRender.com. B) Principal component analysis of the gut microbiota composition in 1479 samples collected from 96 of preterm infants over the first 80 days of life. Points are colored by postnatal age at sample collection and centroids of each postnatal age bin is plotted. Smoothed Shannon diversity is extrapolated based on the observed data distribution and plotted into the background. C) Prevalence over postnatal days for nine selected taxa. D) Number of pairwise strain sharing events (ANI>99.999 and breadth >0.5) across unrelated preterm infant pairs for the taxa with most such events. The number of infants metagenomically positive for the selected taxa is plotted as squares. ***, p<0.001 for S. epidermidis versus all other listed species. *, p<0.05 for C. difficile versus all species listed below it. Pairwise Chi-Square with post-hoc pairwise test with Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment. E) Network representation of strain sharing events for the two taxa with most such events across unrelated infant pairs. Each dot represents a unique preterm infant and is colored by its geographic location. F) Impact of antibiotic exposure on the prevalence of S. epidermidis (top) and C. difficile (bottom) across the entire control cohort over the first 80 days of life. Line patterns correspond to antibiotic category.
