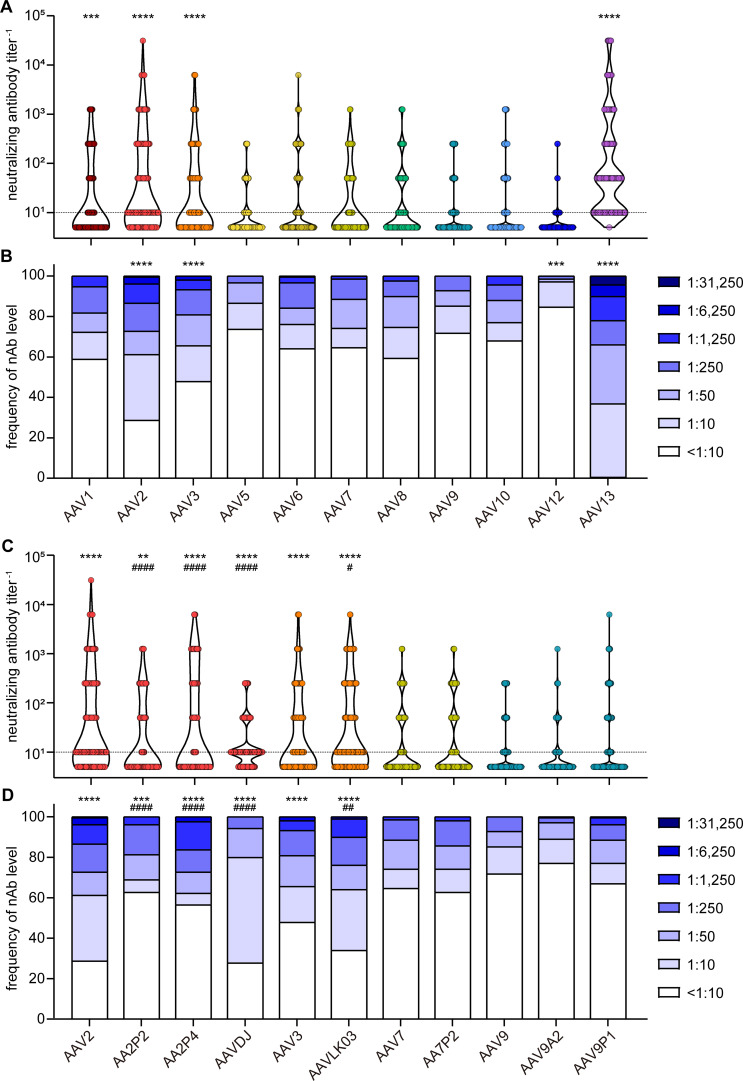
Figure 3.
Neutralizing antibody levels and prevalence. All 209 serum samples of patients with NMD and healthy controls were tested for neutralizing antibodies (nAb) against the indicated AAV with wild-type capsids (A, B) or with peptide-modified or shuffled capsids (C, D). Shown are individual nAb titers (A, C) and the frequency of nAb titers in the cohort (B, D). Values shown in (C, D) for AAV2, AAV3, AAV7 and AAV9 are identical to (A, B) and shown for ease of reference. Each dot (A, C) represents one individual sample, violins indicate the data distribution, the dashed line indicates the detection limit. Significant differences in neutralizing antibody levels compared to AAV9 are indicated by asterisks [** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001; Friedman one-way ANOVA on ranks with Dunn´s multiple comparisons test (A), or Chi square test with Bonferroni adjustment for multiple comparisons (B)], significant differences compared to the parental AAV (C, D) are indicated by pound symbols [# p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, #### p < 0.0001; Friedman one-way ANOVA on ranks with Dunn´s multiple comparisons test (C) or Chi square test with Bonferroni adjustment for multiple comparisons (D)].