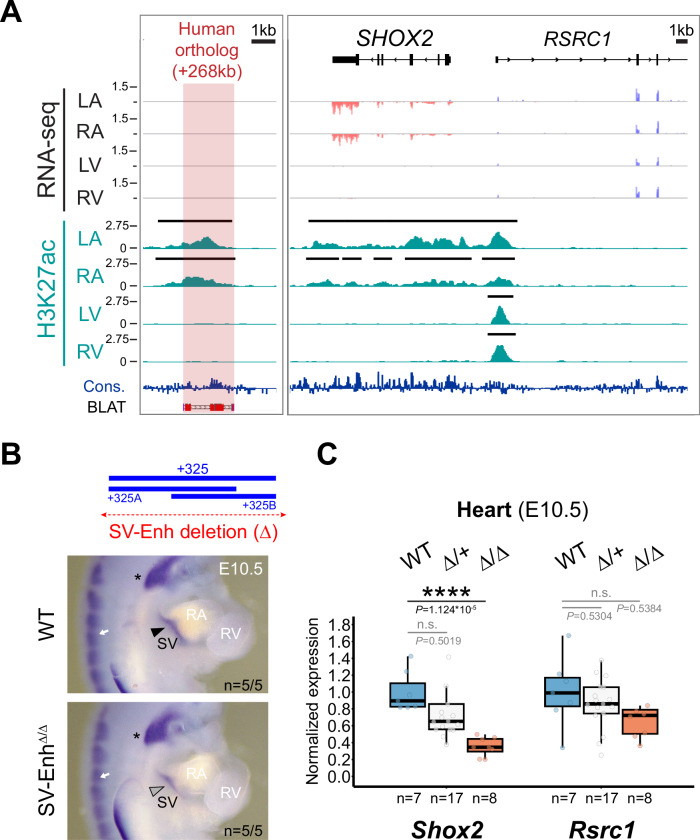
Fig. 5. Enhancer-mediated transcriptional robustness safeguards Shox2 in the heart.
A H3K27 acetylation ChIP-seq (H3K27ac) and RNA-seq profiles from human fetal heart compartments at post conception week 17 (pcw17) across the human orthologous sequence of the +325-mouse sinus venosus (SV) enhancer and the SHOX2 interval. The left ventricle (LV) dataset has been previously published115. +268, distance to SHOX2 TSS. Cons, mammalian conservation by PhyloP. B Top: Generation of a + 325 SV enhancer deletion (4.4 kb) allele in mice (SV-EnhΔ). Below: Shox2 mRNA distribution (ISH) in SV-EnhΔ/Δ compared to WT mouse embryos at E10.5. Arrowhead points to downregulated Shox2 in the SV. Asterisk and arrow mark Shox2 expression in the nodose ganglion of the vagus nerve and dorsal root ganglia (DRG), respectively. C qPCR analysis of Shox2 and Rsrc1 mRNA levels in SV-EnhΔ/+ and SV-EnhΔ/Δ embryonic hearts at E10.5 compared to WT controls. Box plot indicates interquartile range, median, maximum/minimum values (bars) and individual biological replicates (n). P-values are shown, with ****P < 0.0001 (two-tailed, unpaired t-test). Three outliers, two datapoints of Shox2 Δ/+ replicates and one for Rsrc1 (Δ/Δ), are outside of the scale shown. N.s., not significant. “n” indicates number of biological replicates analyzed, with similar results. LA, left atrium. RA, right atrium. RV, right ventricle. Source data are provided in the Source Data file.