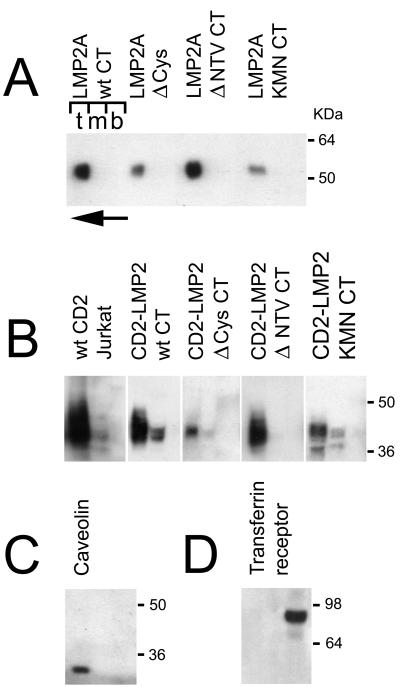
FIG. 5.
Optiprep gradient fractionation of different membrane compartments from HEK 293 cells expressing either LMP2A (A) or CD2-LMP2 CT chimeric membrane proteins (B). Three fractions were collected, one each from the top, middle, and bottom layers of the gradient (indicated by the letters t, m, and b above the left gradient shown in panel A). The direction of flotation of the lighter membrane fraction, not solubilized in Triton X-100, is shown with an arrow, pointing from the bottom to the top of the gradient at the top left of panel A. Fractions were collected, treated as described in Materials and Methods, and blotted on PVDF membranes for immunoblotting. (A) Distribution of LMP2A protein in the gradients is shown for the LMP2A wild type and the Δ Cys, Δ NTV, and KMN CT mutants in the full-length LMP2A background. (B) Distribution of CD2-LMP2A CT constructs between Triton X-100-soluble (bottom) and -insoluble (top) membrane fractions is shown. A lysate from the human T-cell line Jurkat was included, to demonstrate that the native CD2 molecule distributes similarly to the chimeric constructs used in this study. (C and D) Locations of two control proteins, endogenously expressed in the 293 cells; caveolin which is a marker for the detergent-insoluble glycolipid-enriched membranes (rafts) (C) and transferrin receptor, which is known to distribute in the Triton X-100 soluble phosphatidyl-etanolamine rich part of the membrane (D). Immunoblotting was performed with the appropriate antibodies as described in Materials and Methods.