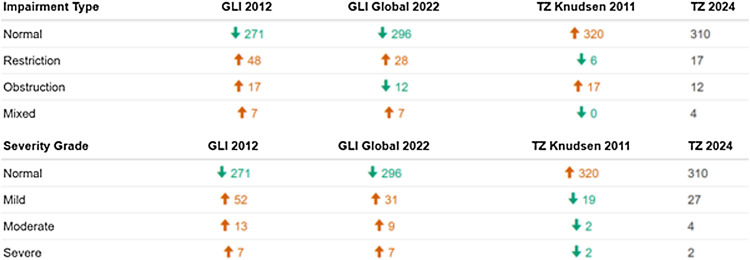
Table 3.
Numbers of participants with different spirometry outcomes (normal, obstruction, restriction or mixed) and severity grades (normal, mild, moderate or severe impairment) based on the Tanzanian reference equations compared to GLI 2012, GLI 2022 and Knudsen et al. 201119 equations. Obstruction severity grading was classified as follows: 1) mild impairment: Z-score ≥−2; 2) moderate: Z-score <−2 and ≥−2.5; 3) severe: Z-score <−2.5. Restriction severity grading was classified as follows: 1) mild impairment: FVC ≥85% LLN FVC; 2) moderate: FVC 55–85% of LLN FVC; 3) severe: FVC <55% of LLN FVC. Using the GLI 2012 and GLI 2022 equations, fewer participants were classified with normal lung function. However, the Knudsen et al.19 equations overestimate participants with a normal lung function. The number of participants with moderate and severe lung impairment was increased using the GLI 2012 and 2022 data but was decreased using the Knudsen et al. equations.19 GLI = Global Lung Initiative; TZ = Tanzania; FVC = forced vital capacity; LLN = lower limit of normal.
|
