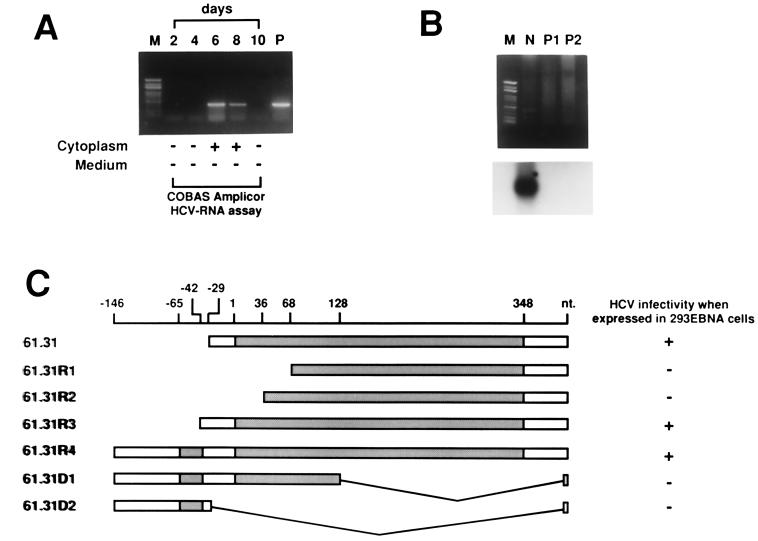
FIG. 3.
Verification of the permissiveness of 61.31 293EBNA cells to HCV infection and determination of the physiological 5′ ends of 61.31 mRNA. (A) HCV-positive serum was used to infect 61.31 293EBNA cells, and HCV RNA was detected every 2 days by RT-nested PCR. The cytoplasmic fractions and the second aliquots of fresh medium used to wash the cells were both subjected to the COBAS Amplicor HCV-RNA assay. (B) Minus-strand-specific RT-PCR for detection of HCV-RNA. M, marker; N, 61.31 293EBNA cells assayed on the 8th day after HCV infection; P1, 50 μl of HCV-positive serum (105 copies/ml); P2, 50 μl of HCV-positive serum (107 copies/ml). The PCR product was verified by Southern blotting (lower panel). (C) Results of the 5′ RACE experiment. Four clones with different 5′ ends are shown (61.31R1 to 61.31R4). The structures of two artificially created deletion mutants are also shown (61.31D1 to 61.31D2). The results of the HCV infection assay for these clones are indicated to the right. Two potential open reading frames, orf-1 (short) and orf-2 (long), are indicated by shaded bars.