Figure 3.
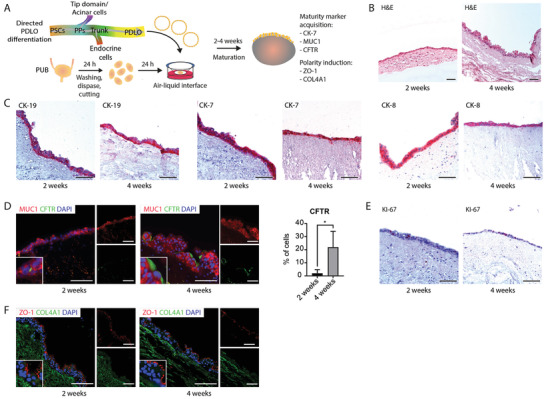
Pancreatic duct‐like organoids mature to adult ductal cells on the porcine urinary bladder. A) Schematic representation illustrating the lineage‐specific generation of pancreatic duct‐like organoids (PDLOs) originated from pluripotent stem cells and their engraftment on the porcine urinary bladder. B) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained histological sections of PDLOs cultured on porcine urinary bladder for two and four weeks (n = 4). C) Immunohistochemistry for duct‐specific cytokeratins CK‐19, CK‐7, and CK‐8 (n = 4) and D) immunofluorescence stainings for ductal maturation marker MUC1 (red) and CFTR (green) on PDLOs cultured on porcine urinary bladder for two and four weeks, with quantification of CFTR‐positive cells (n = 4). Data are shown as mean ± SD. Cells were counterstained with DAPI (blue). *, p < 0.05. E) Immunohistochemistry staining for KI‐67 on PDLOs cultured on porcine urinary bladder for two and four weeks (n = 4). F) Immunofluorescence stainings for cell polarity marker ZO‐1 (red) and COL4A1 (green) in PDLOs cultured on porcine urinary bladder for two and four weeks (n = 4). Scale bars represent 100 µm. PPs, pancreatic progenitors; PSCs, pluripotent stem cells; PUB, porcine urinary bladder.
