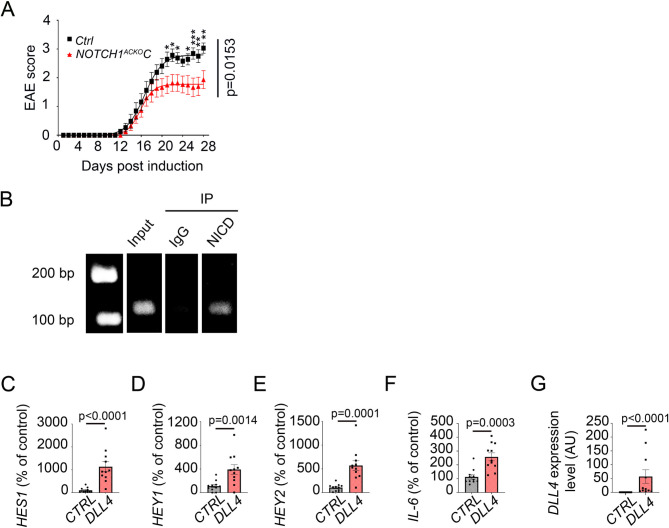
Fig. 4.
DLL4-NOTCH1 signaling in reactive astrocytes promotes IL-6 transcription via a direct interaction with NICD. (A) Notch1ACKOC mice and control mice induced with EAE were scored daily according to a widely-used 5-point scale (EAE scoring: 1 limp tail; 2 limp tail and weakness of hind limb; 3 limp tail and complete paralysis of hind legs; 4 limp tail, complete hind leg and partial front leg paralysis). Statistical significance was determined by using a 2 ways Anova test followed by the Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test, (*: p ≤ 0.05; **: p ≤ 0.01; ***: p ≤ 0.001 ****: p ≤ 0.0001). (Notch1ACKOC n = 15, WT n = 16). (B) NA were cultured until confluence and treated with IL-1β 10ng/mL for 24 h. A Chromatin Immuno-Precipitation (ChiP) was then performed on NA lysates using NICD antibody versus IgG controls to pull-down. IL-6 DNA expression level was then quantified by PCR. (C-G) NA were cultured until 70% confluence. They were then transduced with an empty lentivirus (6.21 108 PFU/mL) versus a DLL4-expressing lentivirus (4.14 108 PFU/mL) and harvested 24 h post transduction (n = 11). (C) HES1, (D) HEY1, (E) HEY2, (F) IL-6 and (G) DLL4 expression were quantified by qRT-PCR. β-ACTIN was used as a reference. Statistical significance was determined by using a Mann-Whitney U test