Figure 1.
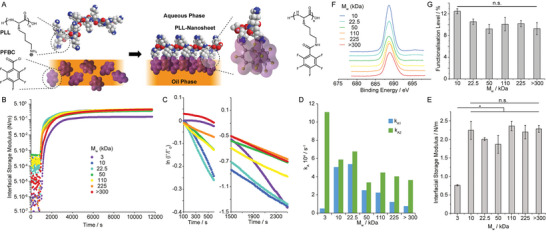
Impact of molecular weight on PLL nanosheet assembly at liquid–liquid interfaces. A) Molecular structure of PLL nanosheets and proposed resulting architecture. B) Evolution of the interfacial shear storage modulus of PLL nanosheets forming at Novec 7500‐water interfaces (Novec 7500 containing 10 µg mL−1 PFBC; aqueous solution is PBS with pH adjusted to 10.5; strain of 10−3 rad and 0.1 Hz). PLL with different Mw (3, 10, 22.5, 50, 110, 225, and >300 kDa) was introduced (after 900 s of equilibration) to make a final solution with a concentration of 100 µg mL−1. C) Corresponding ln(Γ(t)/Γ0) plots at two different time intervals following protein injection. D) Adsorption rate constants extracted from corresponding linear fits. E) Interfacial storage moduli as a function of M w of PLL, measured from frequency sweeps at a strain of 10−3 rad and 0.1 Hz. Error bars are s.e.m.; n = 3. F) XPS spectra (F 1s) obtained for nanosheets generated with PLL with different M w. G) Functionalization levels quantified from corresponding XPS data (error bars are s.e.m.; n = 3). One‐way ANOVA; n.s., non‐significant; *p < 0.05.
