Figure 8.
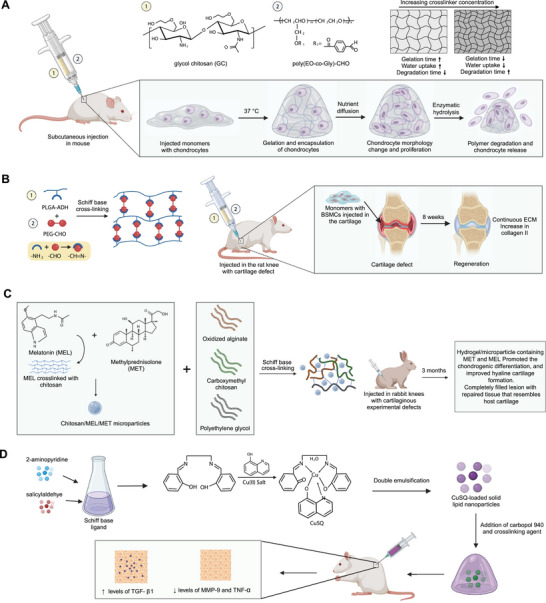
Schiff base mediated crosslinked hydrogel. A) Formation of poly(ethylene oxide‐co‐glycidol)‐CHO ((poly(EO‐co‐Gly)‐CHO)) and glycol chitosan‐based injectable hydrogel crosslinked using the Schiff base reaction. The degradable hydrogel provided a suitable microenvironment for oxygen and nutrient exchange for the proliferation of chondrocytes. B) In situ self‐crosslinking of PLGA/PEG hydrogels. Injecting hydrogels with BMSCs in the cartilage increased collagen II and promoted extracellular matrix formation. C) Injectable in situ forming microparticle/hydrogel system consisting of small molecule drugs, melatonin, and methylprednisolone crosslinked with chitosan using ionic gelation to form microparticles. The microparticles were added in the hydrogel system of oxidized alginate, carboxymethyl chitosan (CMC), and polyethylene glycol, crosslinked through the Schiff base reaction between the amine group of CMC and aldehyde group of oxidized alginates. The hydrogel injected in vivo model with cartilaginous experimental defects promoted chondrogenic differentiation, and improved hyaline cartilage formation. D) Injectable hydrogel loaded with Schiff base CuSQ solid lipid nanoparticles to express enhanced TGF‐β1 and reduced levels of MMP‐9. Schiff base CuSQ was formulated using 2‐aminopyridine, salicylaldehyde, and Cu(II) salt.
