Figure 4.
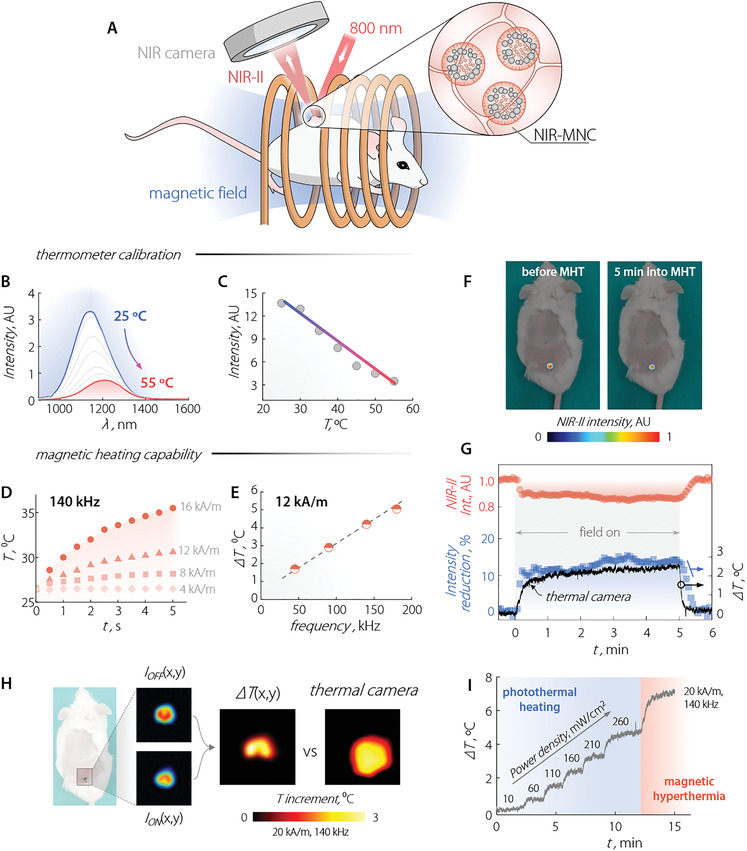
A) Scheme of the setup used for in vivo MHT experiments. B) NIR‐II emission spectra of a colloidal dispersion of NIR‐MNCs (in water) under a 1 mm layer of murine skin at different temperatures. λex = 800 nm. C) Temperature dependence of the integrated emission intensity of the NIR‐MNCs under ex vivo murine skin. The temperature was recorded with the aid of a thermocouple. Symbols are data obtained from the analysis of the emission spectra and the solid line is a guide for the eye. D) Temporal evolution of the temperature of a colloidal dispersion of NIR‐MNCs in water for different AC magnetic field intensities with a frequency of 140 kHz. E) Temperature increment induced in a colloidal dispersion of NIR‐MNCs subjected to a 12 kA m−1 AC magnetic field for different frequencies. Solution temperature was registered by an optical fibre thermal sensor. F) NIR‐II fluorescence images of a CD1 mouse subjected to intradermal injection of NIR‐MNCs before and 5 min after the application of a 20 kA m−1 magnetic field of 100 kHz frequency. G) Temporal evolution of the intradermal NIR‐II emission intensity (orange) and the relative reduction in the NIR‐II intensity (blue) during the application of a 20 kA m−1, 100 kHz AC magnetic field for 5 min. The relative intensity reduction was converted to a relative change of the intradermal temperature using the calibration curve reported in (C). For the sake of comparison, in (F), the thermal readout obtained with an infrared thermal camera is also reported (black line). H) Intradermal thermal image obtained in the presence of a 20 kA m−1, 140 kHz AC magnetic as obtained from the NIR‐II fluorescence images obtained in the presence and absence of the magnetic field. Cutaneous thermal images acquired with an infrared thermal camera are also included. I) Temporal evolution of the intradermal temperature during the application of subsequent photothermal and hyperthermia processes as obtained from a thermal camera.
