Figure 1.
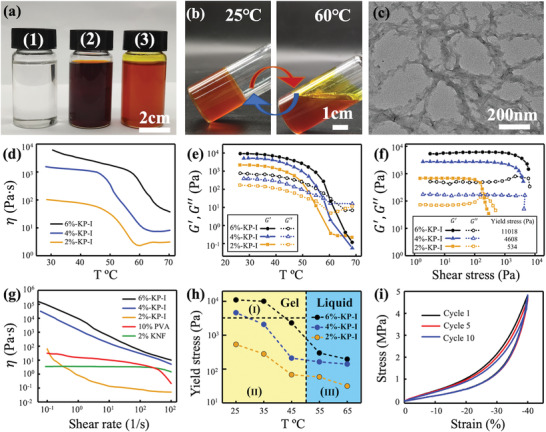
Preparation and characterization of KNF‐PVA inks (KP‐I). a) Mixing transparent 1) PVA/DMSO and dark 2) brown KNF/DMSO solutions yielded 3) orange KNF‐PVA inks. b) Transition of KP‐I between the gel (25 °C) and liquid (60 °C) state. c) TEM image of KP‐I. d) Temperature‐dependence of viscosity for KP‐I with different total concentrations. e) Dynamic modulus of KP‐I measured at different temperatures. f) Yield stress of KP‐I characterized by measuring storage (G′) and loss (G″) modulus at increasing shear stress values. g) Shear‐rate dependent viscosity of KNF‐PVA inks, PVA in DMSO solution (PVA/DMSO) and KNF in DMSO solution (KNF/DMSO). h) Determining printable temperatures (Region II) of KP‐I. Symbols were yield stress values of KP‐I measured at different temperatures, the vertical dashed line indicated the gel‐liquid transition temperature (≈50 °C) of KP‐I, and the horizontal dashed line marked the maximum shear stress generated in the 3D printer. KP‐I was in the gel state in Region I and II, and became liquid in Region III. i) Ten repeated cyclic stress–strain curves for 4%‐KP‐I. All measurements were conducted at 25 °C unless otherwise specified.
