Figure 5.
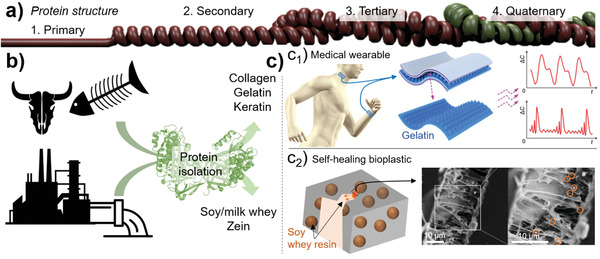
Extraction of soluble proteins from FLW. a) The properties of proteins are structurally dependent and in the native state they occur as tertiary or quaternary structures (Reproduced with permission.[ 356 ] Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society). Their extraction is usually associated with a protein deconstruction into lower structural order, e.g., from tertiary to secondary. b) Valuable protein fraction such as collagen, gelatin, milk whey, and keratin can be obtained from animal‐based FLW, while soy whey and zein can be extracted from crop‐derived FLW. c) Such proteins can be used to obtain advanced materials such as c1) gelatin‐based wearable tactile sensors to monitor physiological signals or physical motions (Adapted with permission.[ 357 ] Copyright 2020, John Wiley & Sons) and c2) soy whey‐loaded microcapsules (orange spheres) incorporated into PLA to introduce self‐healing properties (Adapted with permission.[ 358 ] Copyright 2016, John Wiley & Sons).
