Figure 8.
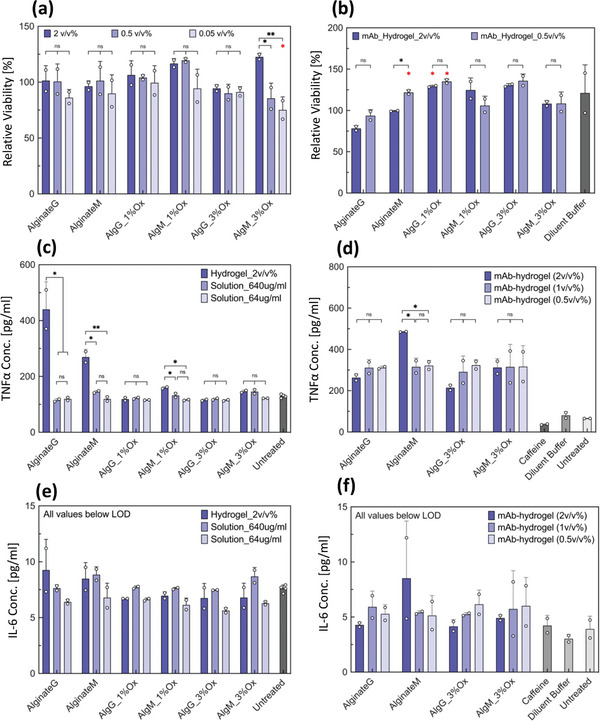
In vitro cell based studies using RAW 264.7 mouse macrophage cells in the presence of alginate hydrogel particles. a) Cell viability after exposure to alginate hydrogel particles (blank). b) Cell viability after exposure to crystalline monoclonal antibody (mAb) laden hydrogel particles. Viability of cells treated with each alginate type was compared with that of untreated cells for statistical analysis. c) Tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) concentration in the supernatant of alginate hydrogel particles. d) TNFα concentration in the supernatant of crystalline mAb‐laden alginate hydrogel particles. e) Interleukin‐6 (IL‐6) concentration in the supernatant of alginate hydrogel particles. f) IL‐6 concentration in the supernatant of crystalline mAb‐laden alginate hydrogel particles. Crystalline mAb‐laden hydrogel particles were prepared at 100 mg mL−1 particle loading. Up to 2 v/v % of alginate particles per cell media was tested. For (c) and (e) solution Solution of sodium alginate was also tested at 640 and 64 µg mL−1 to simulate an exaggerated effect of degradation and dissolution of the hydrogel particles on the cells. For all (e) and (f) samples, the concentration was below the limit of detection of the ELISA. Samples in duplicate. Data were compared using one‐way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. Adjusted p values were indicated as: **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, ns > 0.05. Statistical information shown in red indicates comparison with untreated cells; only significant differences are depicted.
