Figure 4.
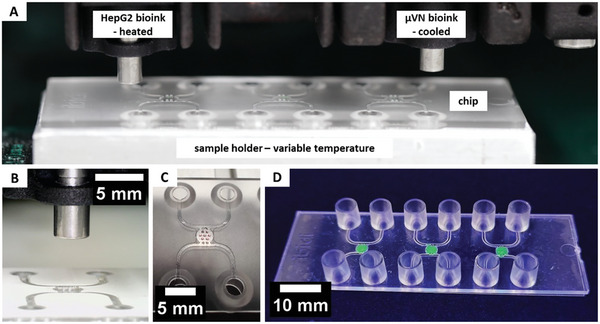
Overview of the printing configuration. The parenchymal bioink containing HepG2 is placed in a heated print head to keep the agarose liquid, while the vasculogenesis bioink is in a cooled print head to prevent fibrinogenesis. The chip is placed on a temperature‐controlled sample holder (A) that ensures repeatable positioning of the chips inside the printer (B). First, seven individual drops of the parenchymal bioink (red) are printed and cooled (C), before the chamber is filled with the vasculogenesis bioink (stained in green for better visualization) and the chip sealed (D).
