Figure 1.
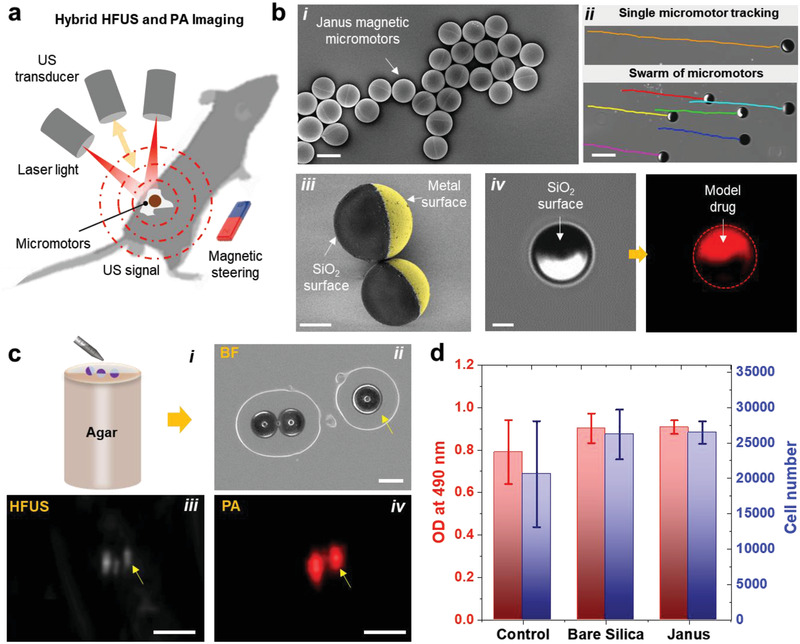
Fabrication and characterization of magnetically driven micromotors. a) Schematic showing the working principle of the employed hybrid HFUS and PA imaging technique. b) Fabrication and functionalization of the micromotors: i) drop‐casted SiO2 particles (⌀ = 100 µm) half‐coated with metal layers (10 nm Ti, 50 nm Fe, and 10 nm Ti) using electron beam deposition. Scale bar: 100 µm. ii) Optical tracking of single and swarm of moving micromotors. Scale bar: 200 µm. iii) Pseudo‐colored SEM image of two half‐coated micromotors and iv) BF and fluorescence images of the functionalized micromotors with a model drug (DOX). Scale bar for iii,iv) 40 µm. c,i) Schematic of an agarose phantom containing the micromotors. Comparison between ii) BF, iii) HFUS, and iv) PA images of single micromotors. Scale bar for BF: 100 µm. These images were acquired at 800 nm, where the fluence was set below the MPE limit of 20 mJ cm−2. Scale bar for HFUS and PA: 1 mm. d) MTS assay showing cell viability of MSCs after being co‐cultured with bare SiO2 and metal‐coated particles to test the cytotoxicity of the employed materials. The control group proceeded without any particles. Each error bar denotes the ±SD from three replicates (n = 3).
