Figure 3.
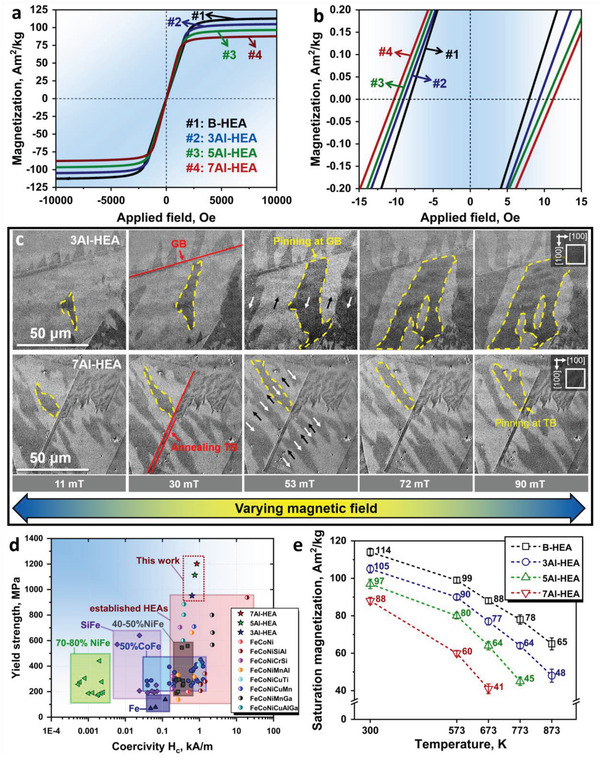
Soft magnetic behavior of the HEAs and associated Bloch wall pinning mechanisms. a) Hysteresis loops acquired up to ±10 000 Oe at room temperature. b) Hysteresis loops measured at a fine step size of 2 Oe per second, showing the coercivity of the alloys. c) Growth of the magnetic domain structure in the 3Al‐HEA and 7Al‐HEA, imaged by Kerr‐microscopy, under external magnetic fields. d) Yield tensile strength–coercivity profiles of the investigated soft magnetic HEAs compared to those of other soft magnetic materials, such as NiFe,[ 54 , 55 ] CoFe,[ 38 , 56 ] SiFe,[ 23 ] Fe,[ 57 ] and established HEAs.[ 14 , 25 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 58 , 59 , 60 ] e) Plot of the temperature dependence of the saturation magnetization of the investigated HEAs.
