Figure 1. Inspiration from aortas.
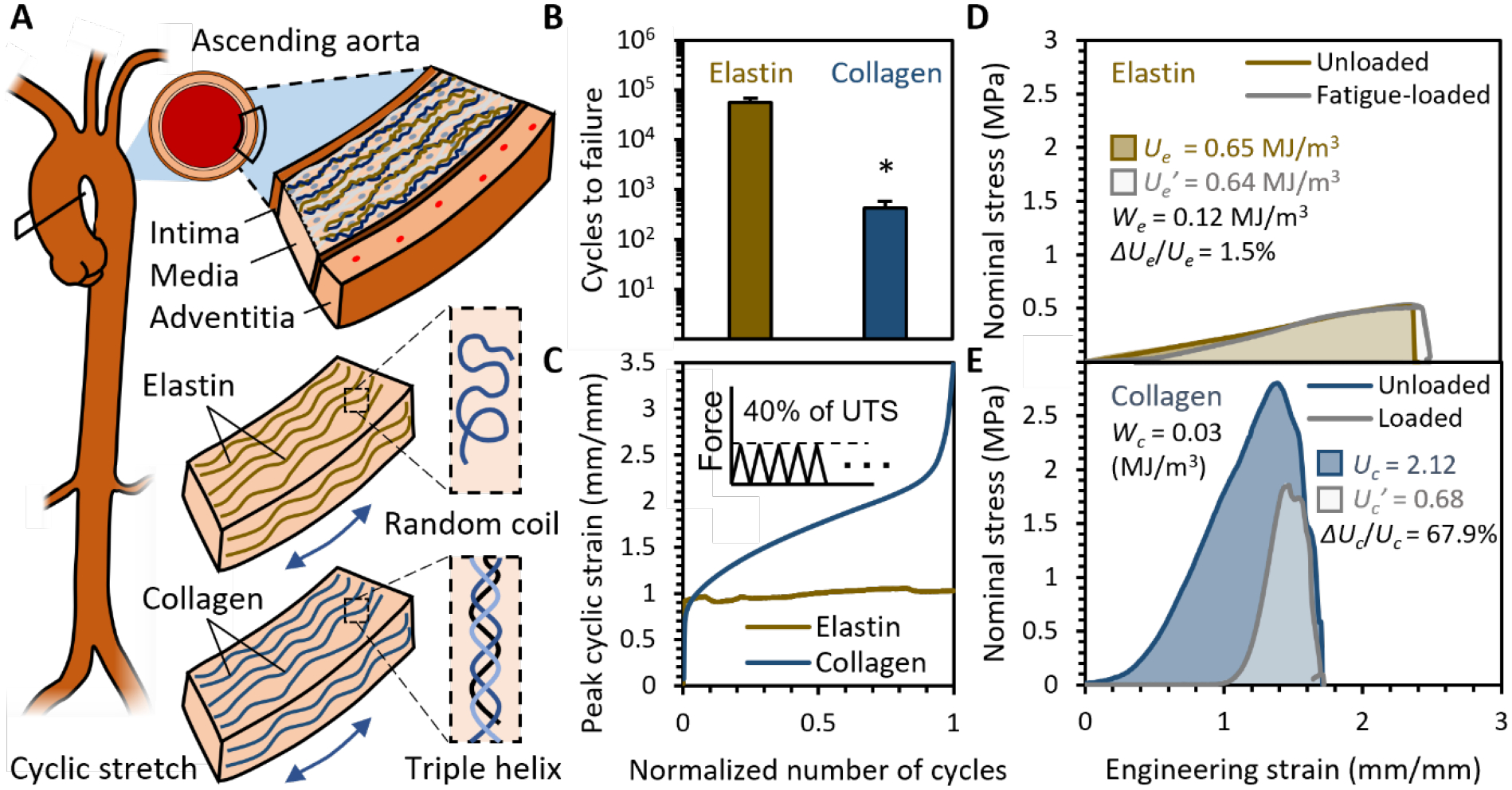
(A) Elastin and collagen isolated from porcine ascending aortas were used as the model to study and define durability for biomaterials and set baselines for maximum fatigue energy density We and toughness consumption ratio ΔU/U. (B) Samples were loaded in creep-fatigue to 40% of their UTS at 1 Hz until tissue failure or 20 hrs. Elastin sustained the loading, while collagen failed within limited cycles. n = 15, *p < 0.05, two tailed student T test. (C) Collagen exhibited creep behaviors, as their peak strain increased with cycles, while elastin did not show creep behavior. (D) Elastin has a small ΔUe/Ue, as its toughness remained the same even after having been loaded to We. (E) Collagen has a large ΔUc/Uc, as its toughness was significantly consumed after having been loaded to Wc.
