Figure 5. Comparison between metastable high-entropy gelatin and gelatin prepared by polymer engineering approaches.
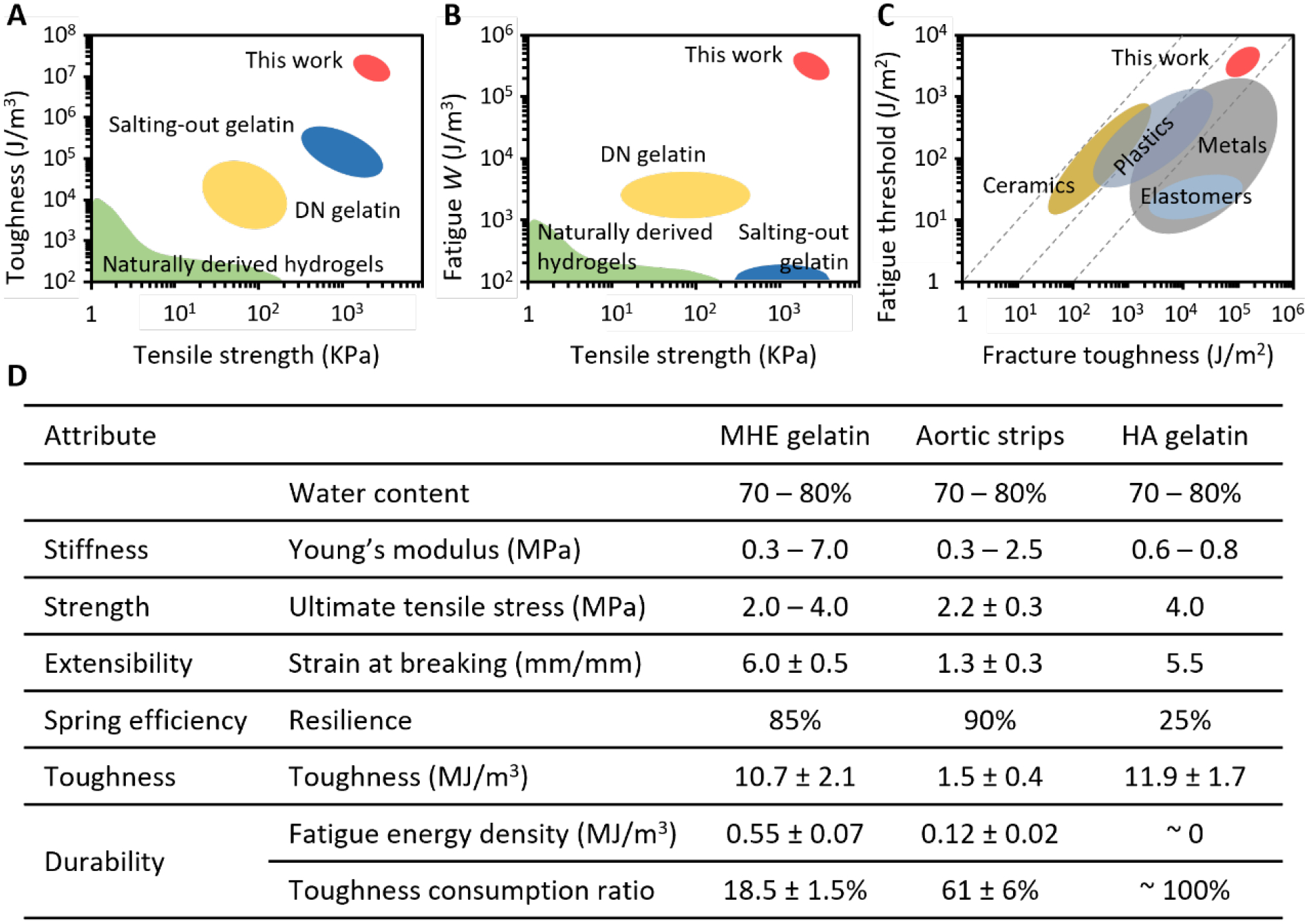
A. Toughness-strength chart compares MHEG to conventionally prepared naturally derived hydrogels,[6b, 36b] various salting-out gelatin[3, 5], various double network gelatin such as GelMA – methacrylated gellan gum,[28] GelMA – methacrylated tropoelastin,[29] and tannic acid treated GelMA.[30] B. Fatigue energy density-strength chart compares MHEG to those hydrogels, whose fatigue resistance is generally on or below 103 J/m3.[14] C. Location of MHEG among various classes of materials,[28] in durability-toughness chart. D. Detailed comparison of mechanical properties between MHEG and hierarchically anisotropic gelatin (HAG), which was produced by freeze casting-assisted salting-out.[3] This method has produced by far the best-performance hydrogels. Circumferential aortic media strips are a reference.
