Abstract
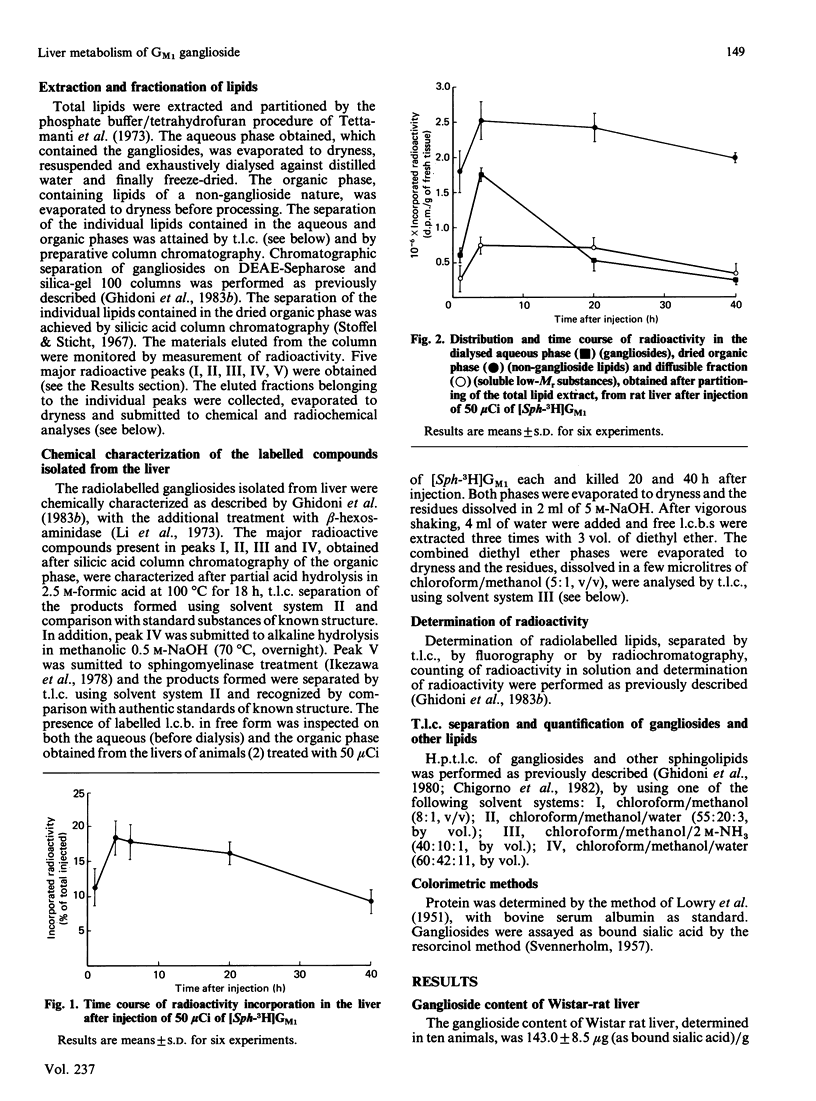
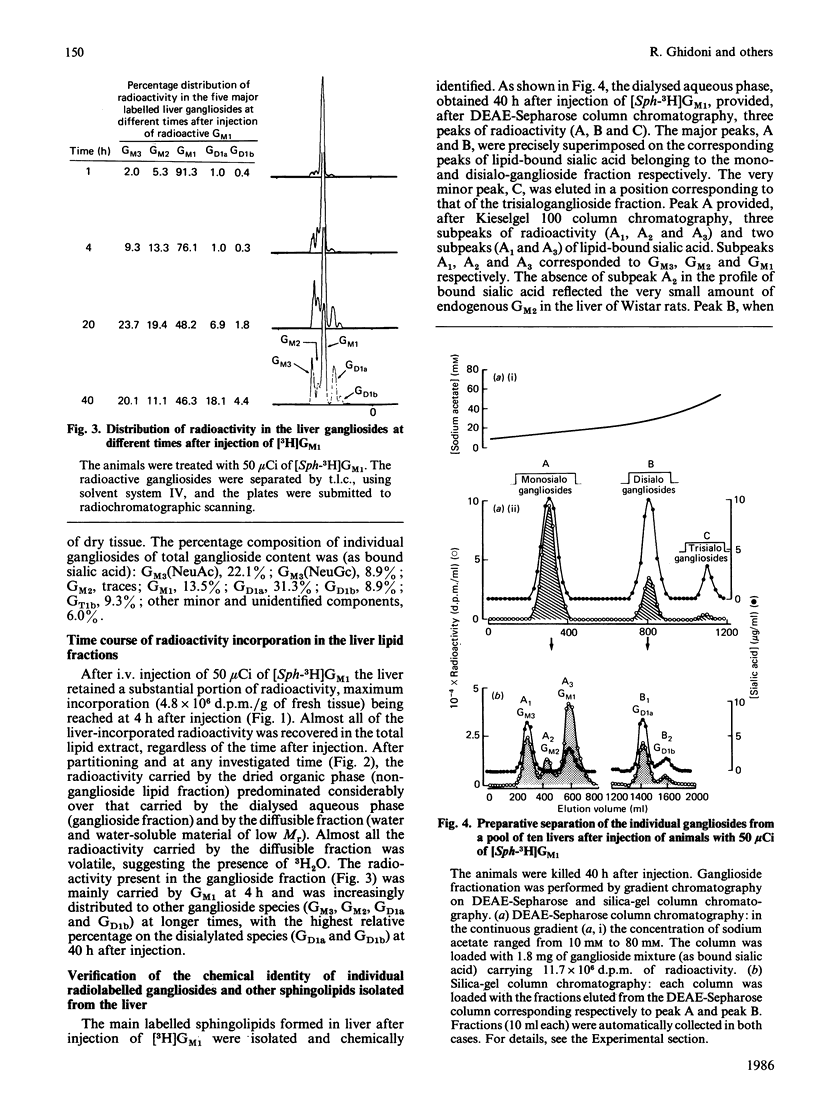
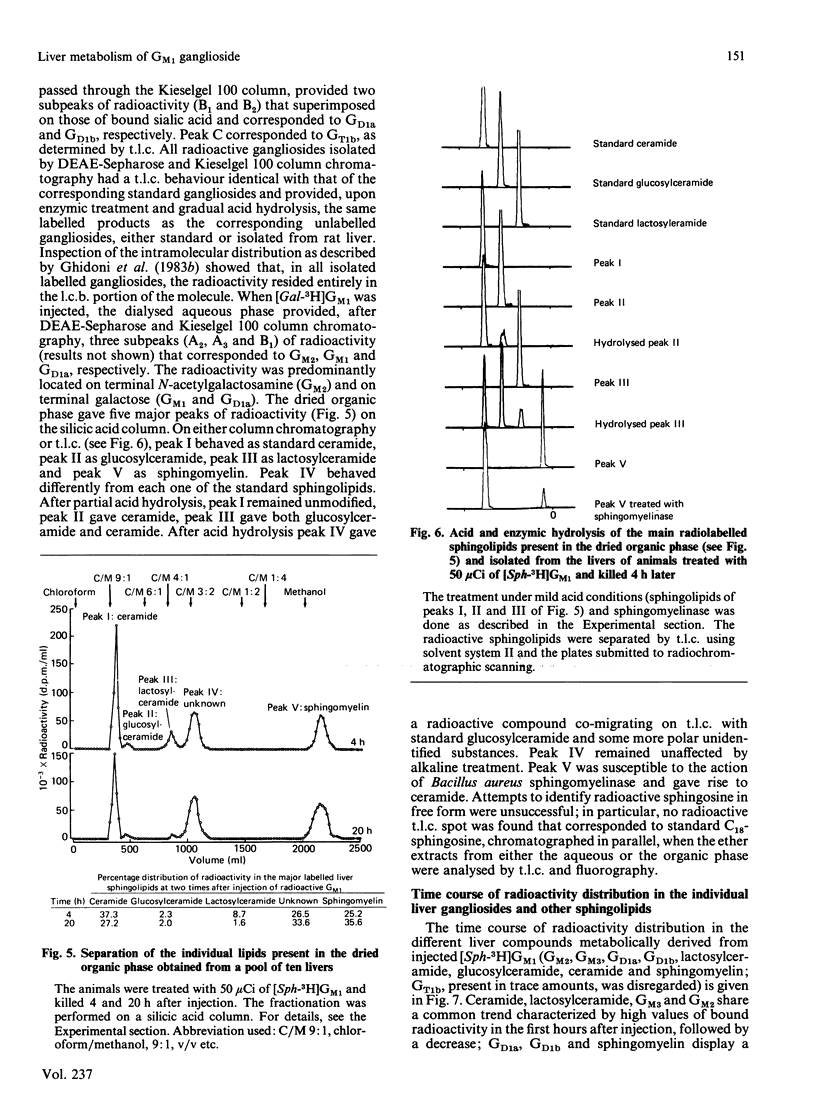
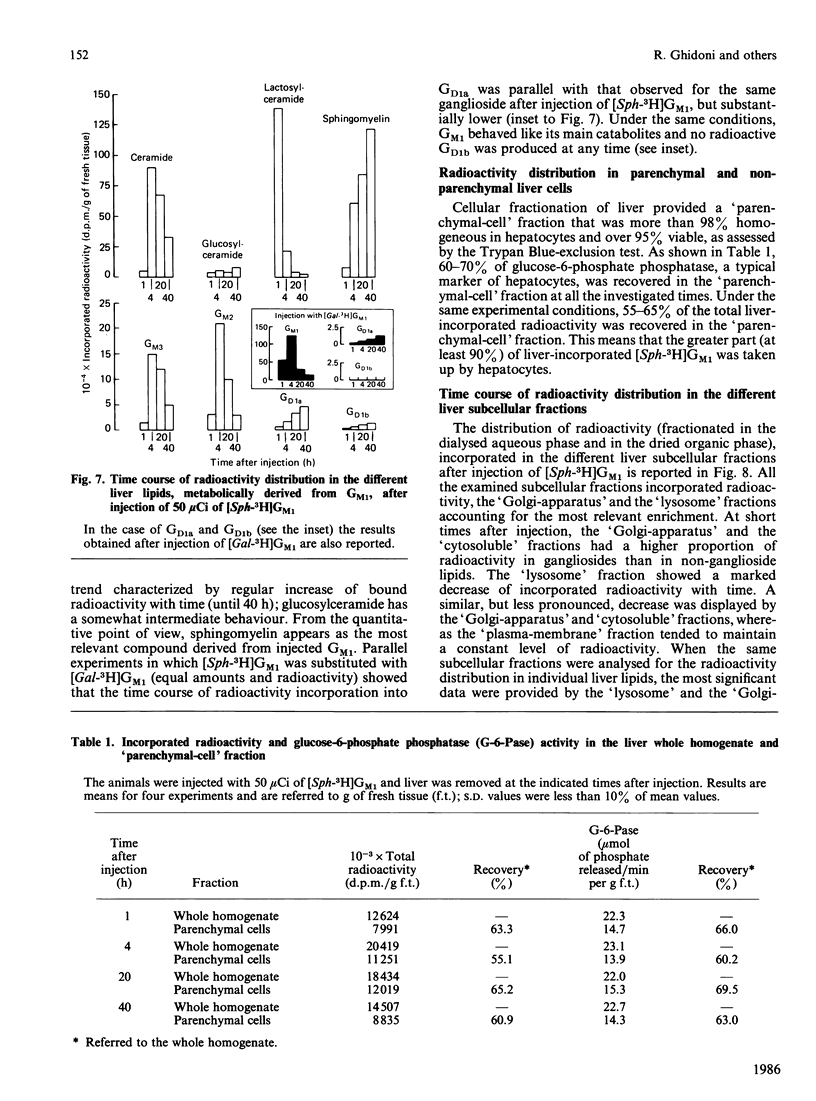
The pathways of metabolic processing of exogenously administered GM1 ganglioside in rat liver was investigated at the subcellular level. The GM1 used was 3H-labelled at the level of long-chain base ([Sph(sphingosine)-3H]GM1) or of terminal galactose ([Gal-3H]GM1). The following radioactive compounds, derived from exogenous GM1, were isolated and chemically characterized: gangliosides GM2, GM3, GD1a and GD1b (nomenclature of Svennerholm [(1964) J. Lipid Res. 5, 145-155] and IUPAC-IUB Recommendations [(1977) Lipids 12, 455-468]); lactosylceramide, glucosylceramide and ceramide; sphingomyelin. GM2, GM3, lactosylceramide, glucosylceramide and ceramide, relatively more abundant shortly after GM1 administration, were mainly present in the lysosomal fraction and reflected the occurrence of a degradation process. 3H2O was also produced in relevant amounts, indicating complete degradation of GM1, although no free long-chain bases could be detected. GD1a and GD1b, relatively more abundant later on after administration, were preponderant in the Golgi-apparatus fraction and originated from a biosynthetic process. More GD1a was produced starting from [Sph-3H]GM1 than from [Gal-3H]GM1, and radioactive GD1b was present only after [Sph-3H]GM1 injection. This indicates the use of two biosynthetic routes, one starting from a by-product of GM1 degradation, the other implicating direct sialylation of GM1. Both routes were used to produce GD1a, but only the first one for producing GD1b. Sphingomyelin was the major product of GM1 processing, especially at the longer times after injection, and arose from a by-product of GM1 degradation, most likely ceramide.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson G. N., Eriksson L. C. Characterization of UDP-galactosyl:asialo-mucin transferase activity in the Golgi system of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 11;570(2):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputto R., Maccioni H. J., Arce A., Cumar F. A. Biosynthesis of brain gangliosides. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;71:27–44. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4614-9_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman P. H., Bradley R. M., Hom B. E., Moss J. Uptake and metabolism of exogenous gangliosides by cultured cells: effect of choleragen on the turnover of GM1. J Lipid Res. 1983 Aug;24(8):1002–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman D. S., Ledeen R. W. Axonal transport of gangliosides in the goldfish optic nerve. Science. 1972 Aug 18;177(4049):630–633. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4049.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatt S. Enzymatic aspects of sphingolipid degradation. Chem Phys Lipids. 1970 Oct;5(1):235–249. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(70)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghidoni R., Sonnino S., Chigorno V., Venerando B., Tettamanti G. Differences in liver ganglioside patterns in various inbred strains of mice. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):885–888. doi: 10.1042/bj2090885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghidoni R., Sonnino S., Chigorno V., Venerando B., Tettamanti G. Occurrence of glycosylation and deglycosylation of exogenously administered ganglioside GM1 in mouse liver. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 1;213(2):321–329. doi: 10.1042/bj2130321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghidoni R., Sonnino S., Masserini M., Orlando P., Tettamanti G. Specific tritium labeling of gangliosides at the 3-position of sphingosines. J Lipid Res. 1981 Nov;22(8):1286–1295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghidoni R., Sonnino S., Tettamanti G., Baumann N., Reuter G., Schauer R. Isolation and characterization of a trisialoganglioside from mouse brain, containing 9-O-acetyl-N-acetylneuraminic acid. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6990–6995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghidoni R., Tettamanti G., Zambotti V. An improved procedure for the in vitro labeling of ganglioside. Ital J Biochem. 1974 Sep-Oct;23(5):320–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikezawa H., Mori M., Ohyabu T., Taguchi R. Studies on sphingomyelinase of Bacillus cereus. I. Purification and properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 27;528(2):247–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamori M., Moser H. W., Kishimoto Y. Specific tritium labeling of cerebrosides at the 3-positions of erythro-sphingosine and threo-sphingosine. J Lipid Res. 1975 Jul;16(4):332–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kint J. A. Fabry's disease: alpha-galactosidase deficiency. Science. 1970 Feb 27;167(3922):1268–1269. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3922.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landa C. A., Defilpo S. S., Maccioni H. J., Caputto R. Disposition of gangliosides and sialosylglycoproteins in neuronal membranes. J Neurochem. 1981 Oct;37(4):813–823. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb04466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. T., Mazzotta M. Y., Wan C. C., Orth R., Li S. C. Hydrolysis of Tay-Sachs ganglioside by beta-hexosaminidase A of human liver and urine. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 10;248(21):7512–7515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh C. H., Plummer D. T. The subcellular localization of acetylcholinesterase and its molecular forms in pig cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1976 Aug;27(2):449–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb12267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller-Podraza H., Bradley R. M., Fishman P. H. Biosynthesis and localization of gangliosides in cultured cells. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 6;21(14):3260–3265. doi: 10.1021/bi00257a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller-Prodraza H., Fishman P. H. Effect of drugs and temperature on biosynthesis and transport of glycosphingolipids in cultured neurotumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 May 22;804(1):44–51. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghavan S., Krusell A., Lyerla T. A., Bremer E. G., Kolodny E. H. GM2-ganglioside metabolism in cultured human skin fibroblasts: unambiguous diagnosis of GM2-gangliosidosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 25;834(2):238–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90161-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roseman S. The synthesis of complex carbohydrates by multiglycosyltransferase systems and their potential function in intercellular adhesion. Chem Phys Lipids. 1970 Oct;5(1):270–297. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(70)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWANT P. L., SHIBKO, KUMTA U. S., TAPPEL A. L. ISOLATION OF RAT-LIVER LYSOSOMES AND THEIR GENERAL PROPERTIES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 6;85:82–92. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. Quantitative estimation of sialic acids. II. A colorimetric resorcinol-hydrochloric acid method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jun;24(3):604–611. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. THE GANGLIOSIDES. J Lipid Res. 1964 Apr;5:145–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito M., Saito M., Rosenberg A. Action of monensin, a monovalent cationophore, on cultured human fibroblasts: evidence that it induces high cellular accumulation of glucosyl- and lactosylceramide (gluco- and lactocerebroside). Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 13;23(6):1043–1046. doi: 10.1021/bi00301a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg P. O., Marzella L., Glaumann H. A method for rapid isolation of rough and smooth microsomes and Golgi apparatus from rat liver in the same sucrose gradient. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Dec;130(2):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of rat liver cells. 3. Enzymatic requirements for tissue dispersion. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Dec;82(2):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90357-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seijo L., Rodriguez de Lores Arna Subcellular distribution of thiamine pyrophosphatase in rat cerebral cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 15;211(3):595–598. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90269-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonderfeld S., Conzelmann E., Schwarzmann G., Burg J., Hinrichs U., Sandhoff K. Incorporation and metabolism of ganglioside GM2 in skin fibroblasts from normal and GM2 gangliosidosis subjects. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):247–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnino S., Ghidoni R., Gazzotti G., Kirschner G., Galli G., Tettamanti G. High performance liquid chromatography preparation of the molecular species of GM1 and GD1a gangliosides with homogeneous long chain base composition. J Lipid Res. 1984 Jun;25(6):620–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W., Sticht G. Metabolism of sphingosine bases, I. Degradation and incorporation of (3-14C)erythro-DL-dihydrosphingosine and (7-3H2)erythro-DL-sphingosine into sphingolipids of rat liver. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Jul;348(7):941–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Suzuki K. Specific radioactive labeling of terminal n-acetylgalactosamine of glycosphingolipids by the galactose oxidase-sodium borohydride method. J Lipid Res. 1972 Sep;13(5):687–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tettamanti G. An outline of ganglioside metabolism. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;174:197–211. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-1200-0_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tettamanti G., Bonali F., Marchesini S., Zambotti V. A new procedure for the extraction, purification and fractionation of brain gangliosides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 19;296(1):160–170. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touster O., Aronson N. N., Jr, Dulaney J. T., Hendrickson H. Isolation of rat liver plasma membranes. Use of nucleotide pyrophosphatase and phosphodiesterase I as marker enzymes. J Cell Biol. 1970 Dec;47(3):604–618. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.3.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


