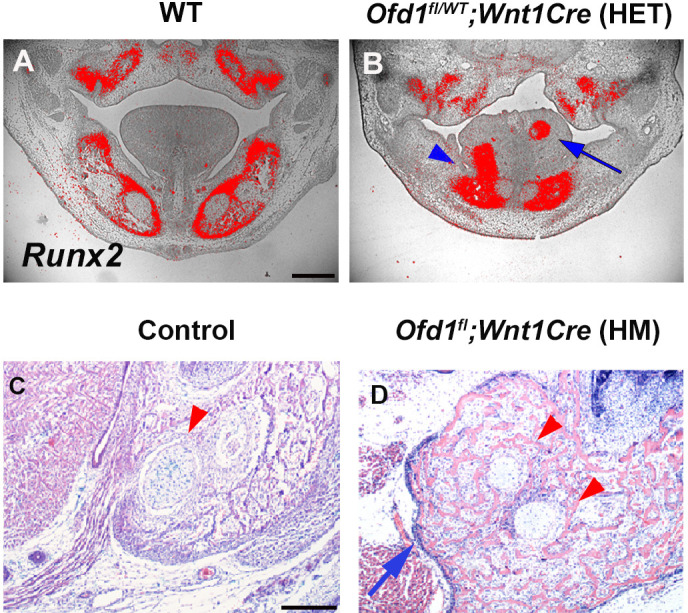
Figure 1. Tongue phenotypes in Ofd1 mutant mice.
(A, B, E–H) Frontal sections showing histological images in wild-type (A, E, G), Ofd1fl;Wnt1Cre(HM) (B) and Ofd1fl/WT;Wnt1Cre(HET) (F–F’’, H) at embryonic day (E) 18.5. Arrow indicating sparse tissue (B). *: tongue (A). Green, blue, and yellow arrows indicating normal muscle, ectopic sparse tissue, and ectopic bone, respectively (F). F’ and F’’ are high magnification of F indicated by blue and yellow arrow, respectively. Arrows indicating tongue frenum region (G, H). The presence of clefts and multiple protrusions; n=58/58. (C, D) Image showing oral view of tongue in wild-type (C) and Ofd1fl/WT;Wnt1Cre(HET) (D). Arrowhead and arrow indicating ectopic protrusion and cleft, respectively (D). Lack of tongue frenum in Ofd1fl/WT;Wnt1Cre(HET); n=30/58. Scale bars: 200 µm (A, B, E, F, G, H), 100 µm (F', F'').
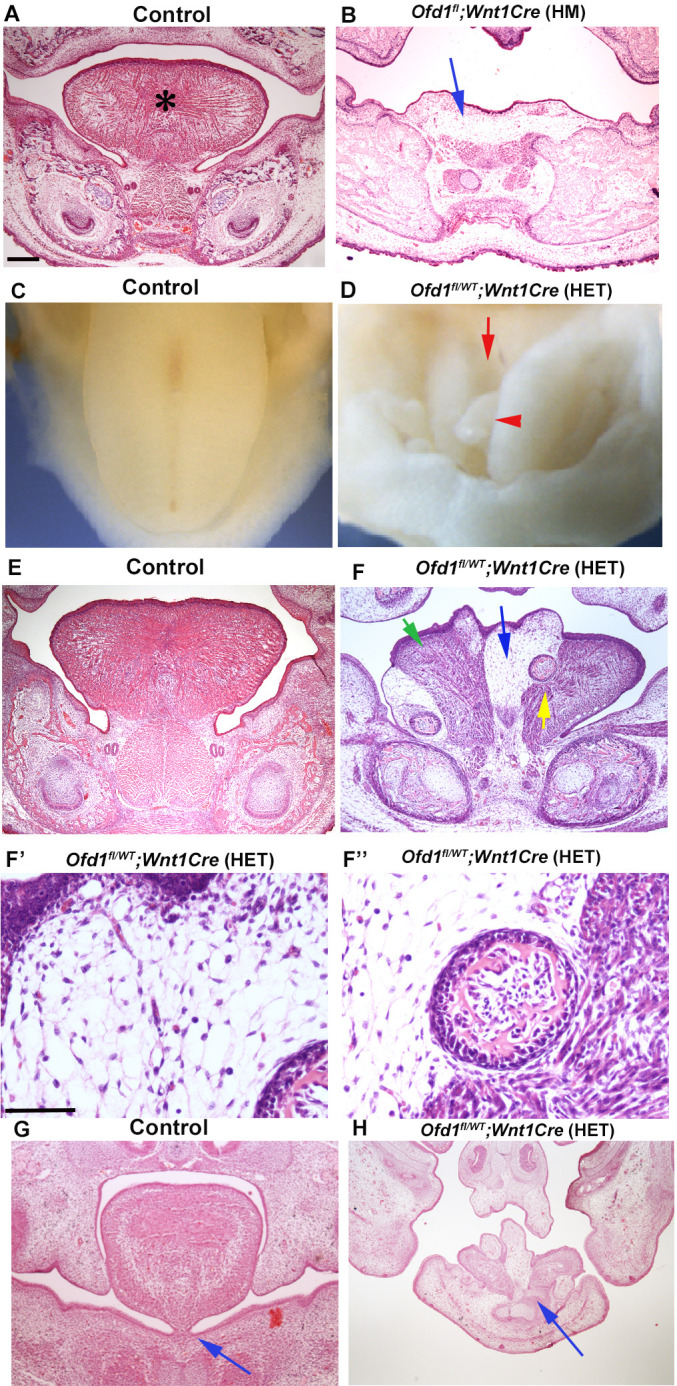
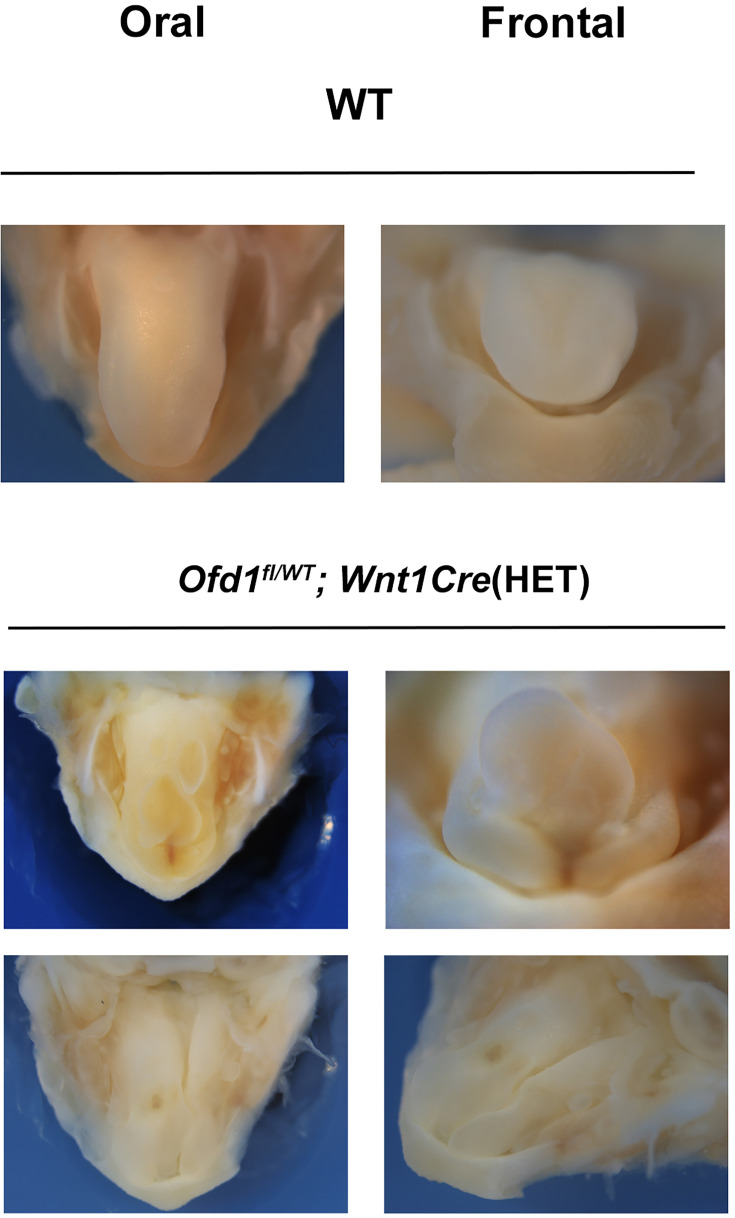
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Abnormal shaped tongue in Ofd1fl/WT;Wnt1Cre(HET) mice.
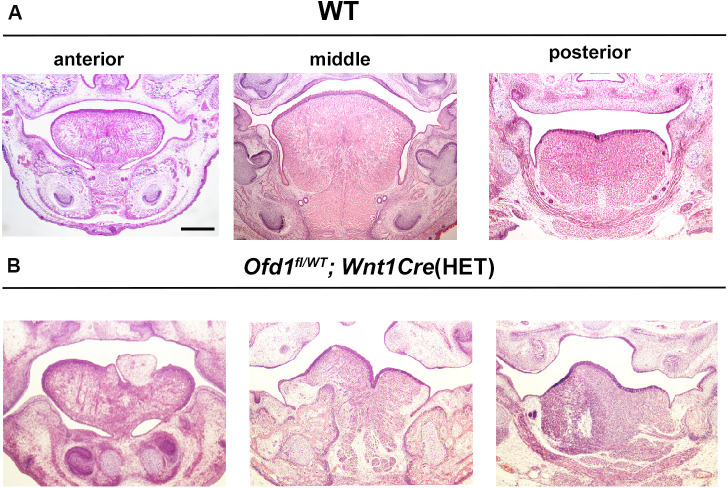
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Bone in tongue of Ofd1fl/WT;Wnt1Cre(HET) mice.