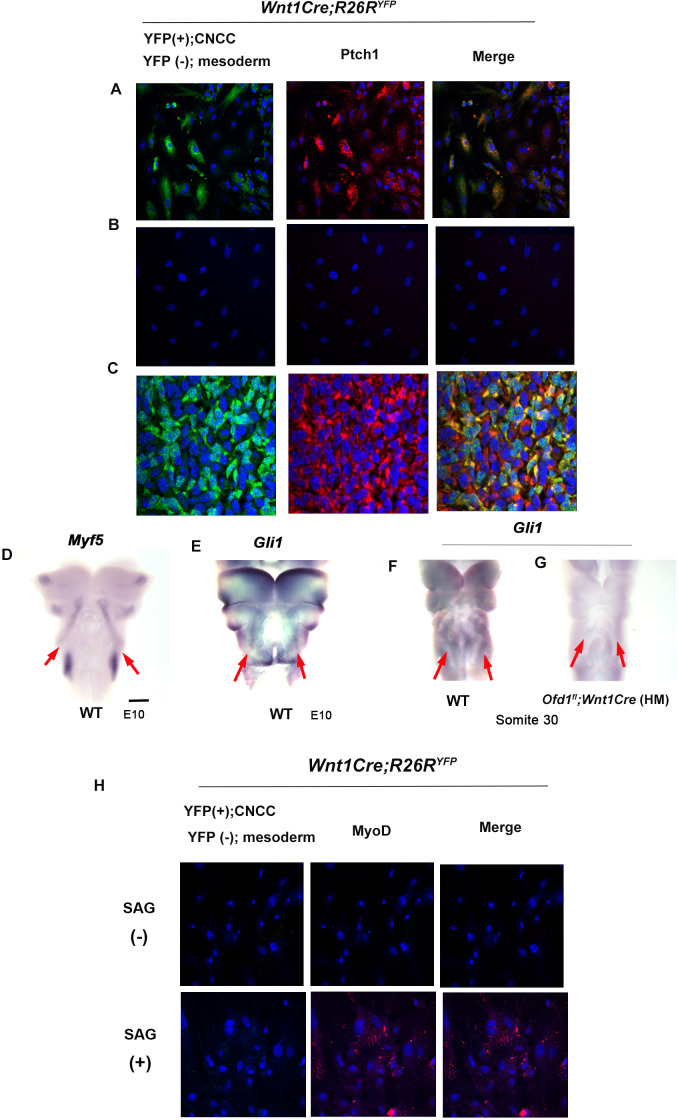
Figure 6. Hh signal in mesoderm-derived cells.
(A, B) Double immunohistochemistry of YFP and Ptch1 on cultured YFP-expressing cranial neural crest-derived cells (CNCC) accompanied by YFP-negative mesoderm-derived cells (A) and only YFP-negative mesoderm-derived cells (B) obtained from Wnt1Cre;R26RYFP mice. (C) Double immunohistochemistry of YFP and Ptch1 in Wnt1Cre;R26RYFP mice. (D–G) Frontal images of whole-mount in situ hybridization of Myf5 (D) and Gli1 (E–G) in wild-type (D–F) and Ofd1fl;Wnt1Cre(HM) (G) at embryonic day (E) 10. (H) Double immunohistochemistry of YFP and MyoD on cultured YFP-negative mesoderm-derived cells obtained from Wnt1Cre;R26RYFP mice with (lower panels) or without (upper panels) SAG. Scale bars: 500 µm (D-G).
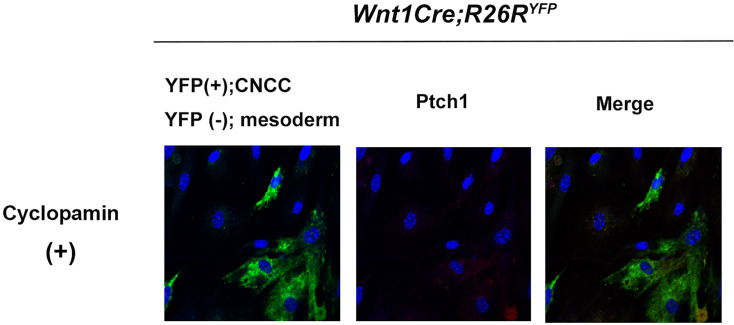
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Cyclopamine treated cranial neural crest-derived cells (CNCC) and mesoderm-derived cells.
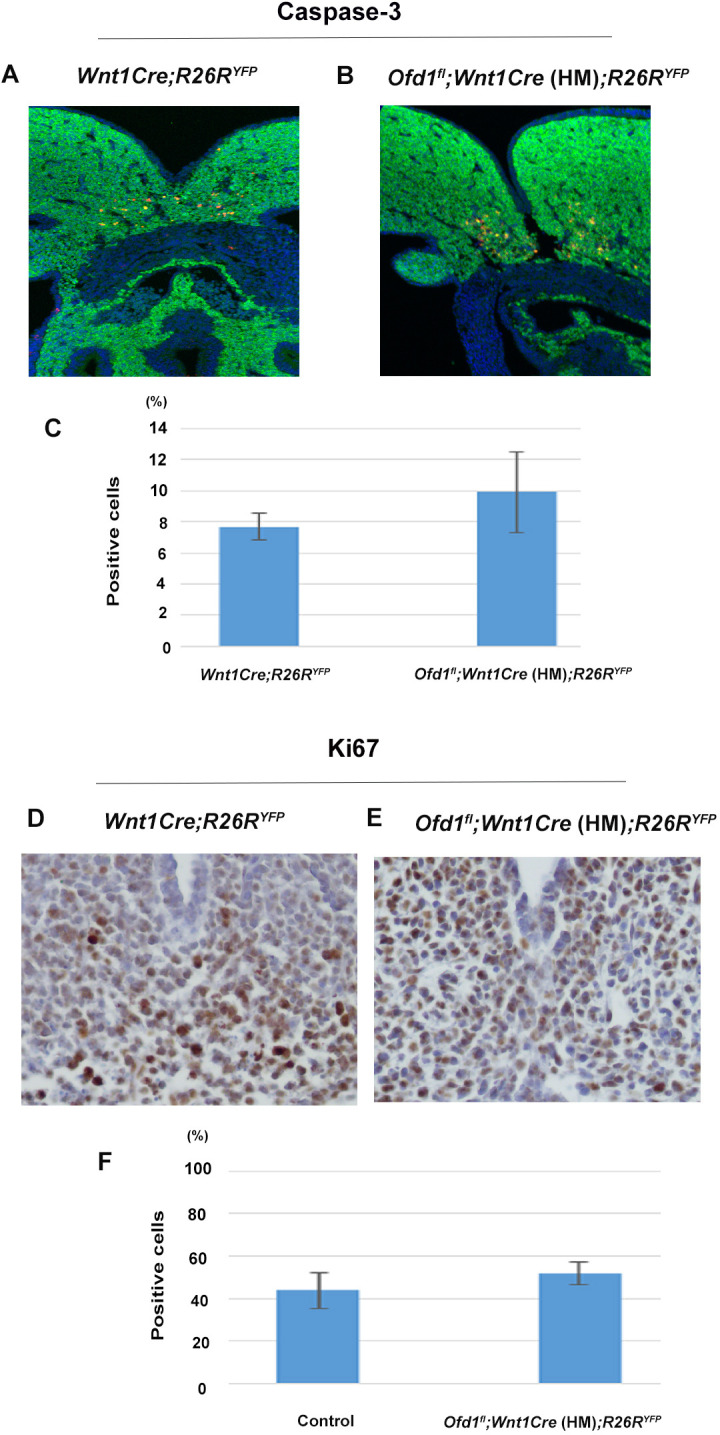
Figure 6—figure supplement 2. Apoptosis and cell proliferation in Ofd1 mutant tongue.