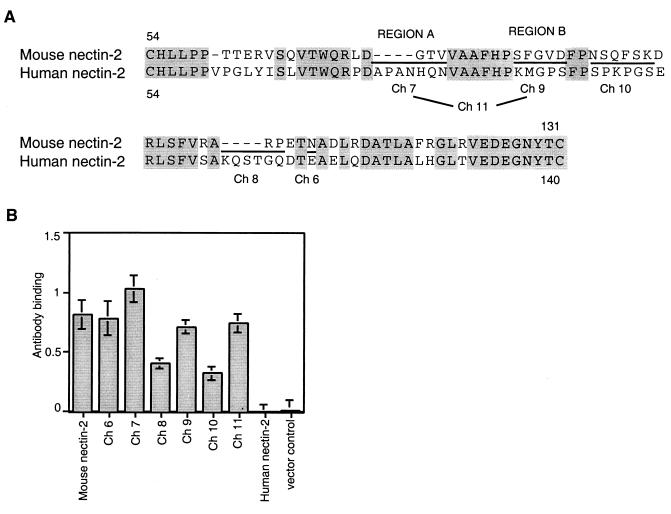
FIG. 3.
Alignment of human and mouse nectin-2 sequences in the V domain and cell surface expression of V domain chimeric molecules. (A) The sequence between the two cysteines of the V domain of mouse nectin-2 is aligned above the corresponding sequence of human nectin-2. Amino acids are numbered from the initial methionine. Gray shading indicates identity between the sequences. New chimeric molecules were constructed by replacing the underlined mouse nectin-2 sequences with the sequences at equivalent positions in human nectin-2 and given the names shown below the human sequence. Ch 11 has both of the substitutions shown for Ch 7 and Ch 9. The amino acids exchanged in Ch 7 and Ch 9 are referred to in the text and later figures as regions A and B, respectively. (B) Cell surface expression of wild-type and V domain chimeric molecules. CHO-K1 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing human nectin-2, mouse nectin-2, or chimeric molecules or with control plasmid and 48 h later tested for the binding of anti-mouse nectin-2 (C2) antibody as explained for Fig. 1. Values shown are the means and standard deviations of triplicate determinations. The same transfected cell populations were used to obtain the results shown in panel B and in Fig. 4.