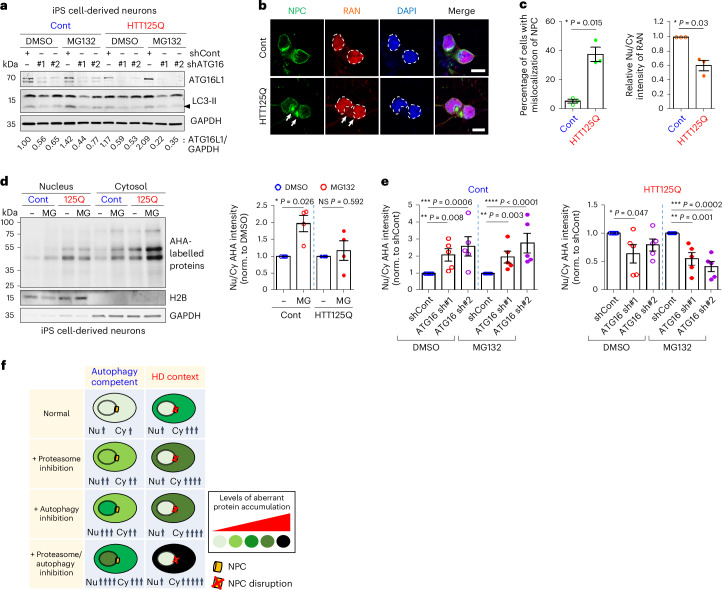
Fig. 4. Cytoplasm-to-nucleus shuttling of bulk proteins is inhibited in Huntington’s disease cells.
a, Inhibition of autophagy using distinct shRNA targeting ATG16L1 (#1 and #2) decreases LC3-II and ATG16L1 levels in control (Cont) and iPS cell-derived neurons from a juvenile patient with HD originally carrying 125 CAGs (HTT125Q) with or without MG132 (MG, 1 µM for 15 h). Representative blot of three biological repeats. b,c, NPC disruption in HTT125Q-derived neurons was detected by staining of either NPC or RAN, compared with Cont iPS cell-derived neurons (b). Arrows indicate the signals of NPC or RAN in the cytoplasm. Scale bar, 10 μm. Quantified data represents mislocalization of NPC (left) or RAN (right) in HTT125Q-derived neurons (c). Values are mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3 independent experiments; *P < 0.05 versus Cont; two-tailed paired t-test). White dashes in b indicate nuclear outline. d, Decreased amount of nuclear-localized newly synthesized proteins (AHA-labelled proteins) in HTT125Q-derived neurons upon MG132 (2 µM for 15 h) treatment, compared with Cont iPS cell-derived neurons. Values are mean ± s.e.m. (n = 4 independent experiments; NS, not significant; *P < 0.05 versus DMSO; two-tailed paired t-test). e, Autophagy compromise exacerbated mislocalization of newly synthesized proteins in cytosol upon MG132 (1 µM for 15 h) treatment in HTT125Q-derived neurons (right) compared to Cont iPS cell-derived neurons (left). Values are mean ± s.e.m. (n = 5 independent experiments; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 versus shCont; one-way ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett test). Data used for one-way ANOVA, where DMSO and MG132 data were not compared, were analysed separately. f, Schematic representation shows idealized protein localization/abundance upon proteasome inhibition, autophagy inhibition or combined proteasome/autophagy inhibition in the HD context. Source numerical data and unprocessed blots are available in source data.