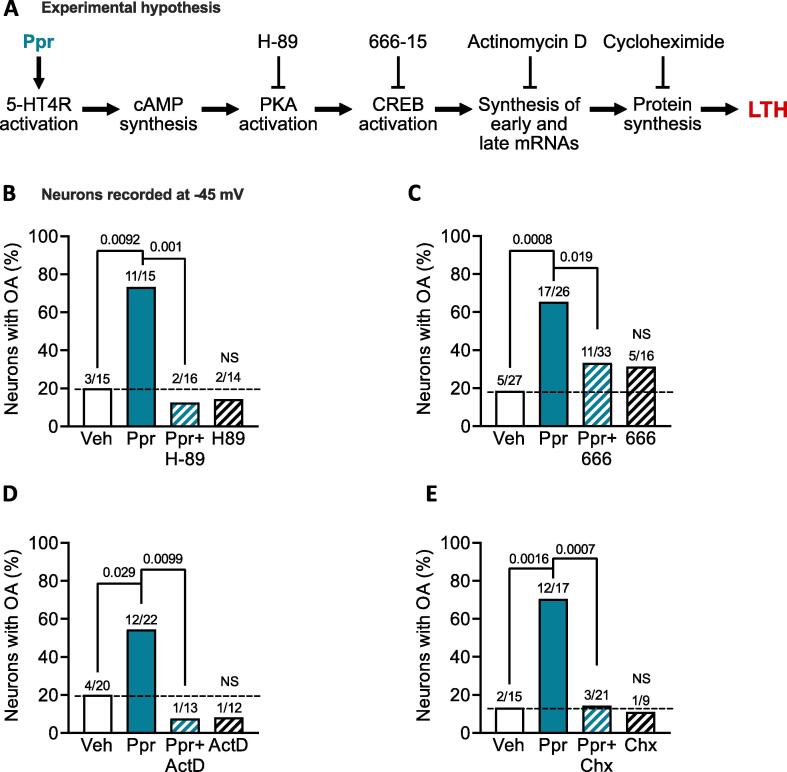
Fig. 3.
Induction of LTH depends upon PKA, CREB, gene transcription, and protein synthesis. A, diagram of the experimental hypothesis with the inhibitors and activators employed for testing. B-E, proportions of neurons with OA at −45 mV treated with either vehicle (0.02 or 0.11 % DMSO, depending upon the inhibitor used), Ppr (1 µM) alone, or (“Ppr + X”) plus an inhibitor of PKA (H-89, 10 µM, B), CREB (666–15, 0.5 µM, C), gene transcription (actinomycin D, ActD, 1 µg/ml, D) or protein synthesis (cycloheximide, Chx, 20 µM, E), and each inhibitor alone. The number of neurons exhibiting OA over the total number sampled is reported above each bar. Comparisons with Fisher’s exact tests followed by Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. For comparisons of OA proportions between Ppr against the vehicle or Ppr + inhibitor, the significance level was * p < 0.025, ** p < 0.005, and *** p < 0.0005 for two comparisons. For vehicle against inhibitor alone, p < 0.05 was considered significant. LTH, long-term hyperexcitability; NS, non-significant; OA, ongoing activity.