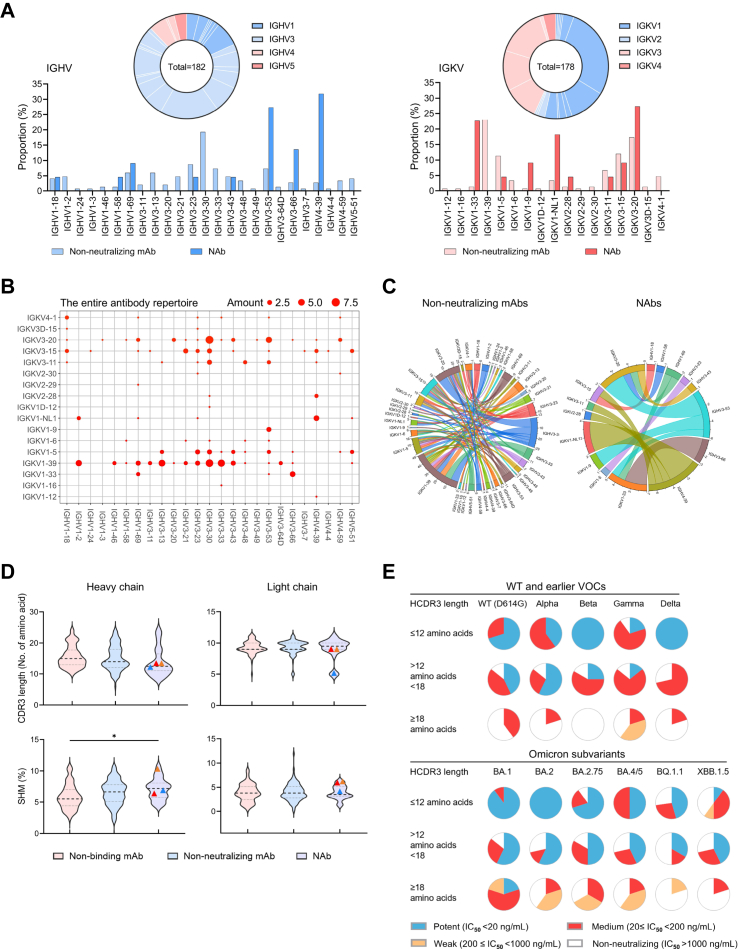
Fig. 2.
Immunogenetic properties of the antibody repertoire induced by Omicron breakthrough infection. (A) Antibody gene repertoire analysis of reactive memory B cells derived from 12 convalescent individuals. In pie charts, the number of all cloned antibody V genes is shown in the center for the heavy (left) or light chains (right). The colors represent variable gene families, and each fragment of the same color stands for one specific sub-family. The histograms summarize the IGHV (left) and IGKV (right) gene usage of 172 recovered mAbs, including 150 non-neutralizing mAbs (non-NAbs) and 22 NAbs, labeled in light and dark colors, respectively. (B and C) Parings of germline heavy and light V genes display preference among NAbs. (B) IGHV and IGKV pairings of 172 recovered mAbs are presented in the bubble diagram and (C) the diversity between non-NAbs and NAbs is indicated in chord diagrams. The outer circle border indicates the number of each pairing. (D) Comparison of CDR3 lengths and SHM rates between recovered non-binding mAbs (n = 64), non-NAbs (n = 86) and NAbs (n = 22). Amino acid lengths and SHM rates compared to germline sequences are presented in violin plots with kernel density estimation curves of the distribution. A dash line and two dotted lines indicate the median and quartiles of each group, respectively. bnAbs ZCP3B4 (red), ZCP4C9 (orange) and ZCP4D5-1 (blue) are presented by symbols. Comparisons were made by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons test. ∗p < 0.05. (E) Neutralizing potency distribution of 22 NAbs against WT (D614G), earlier VOCs and Omicron subvariants. The NAbs are grouped according to their overall CDR-H3 amino acid (aa) lengths as follows: short (≤12 aa, upper panel), intermediate (12–18 aa, mid panel), or long (≥18 aa, lower panel).