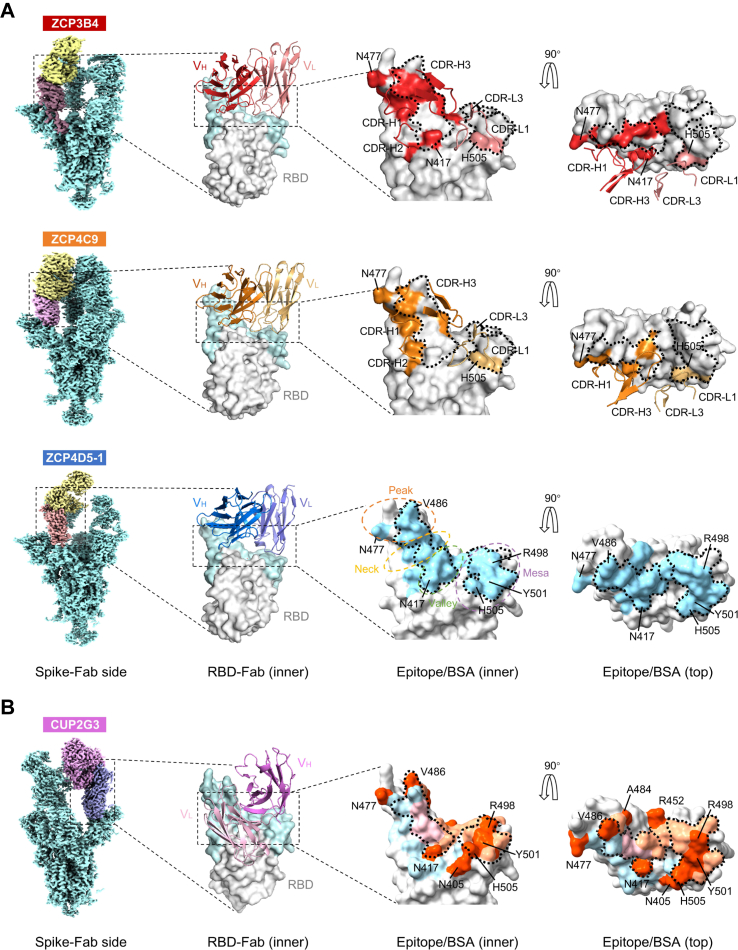
Fig. 4.
Structural basis for class I bnAbs ZCP3B4, ZCP4C9, ZCP4D5-1 and CUP2G3. (A) Binding modes and footprints of ZCP3B4, ZCP4C9 and ZCP4D5-1. Cryo-EM density maps of BA.5 spike trimers in complex with bnAb Fabs are shown in the side views. ‘Up’ RBDs of complexes are colored in dark brown (ZCP3B4), purple (ZCP4C9) and light orange (ZCP4D5-1), whereas bnAb Fabs are colored in yellow. The cartoons represent the structures of bnAb heavy chain and light chain variable regions (VH and VL) binding RBD (gray), viewed from the RBD inner face. The receptor binding motif (RBM) is colored in light cyan. HCDRs and LCDRs of ZCP3B4 and ZCP4C9 involved in the interaction are shown in the zoom-in figures. Epitopes of ZCP3B4 and ZCP4C9 and the buried surface area (BSA) of ZCP4D5-1 are shown in corresponding colors on the RBD surface viewed from the inner and top faces. BA.5 mutation sites involved in epitopes/BSA are also indicated. The RBM is topologically divided into ‘peak’, ‘neck’, ‘valley’ and ‘mesa’ subsections. The ACE2 binding site is outlined with dotted lines. PDB codes: 8K19 (BA.5 RBD-ZCP3B4 Fab) and 8K18 (BA.5 RBD-ZCP4C9 Fab). (B) Binding mode and footprint of CUP2G3. Cryo-EM density map of BA.5 spike trimer in complex with CUP2G3 Fabs is shown in the side view. The ‘up’ RBD of complex is colored in purple and Fab is in pink. The cartoon represents the structure of CUP2G3 heavy chain and light chain variable regions (VH and VL) binding RBD (gray), viewed from the RBD inner face. The receptor binding motif (RBM) is colored in light cyan. The buried surface areas (BSA) buried by VH (light orange), VL (light blue) and both (pink) are viewed from the inner and top faces. BA.5 mutation sites involved in the BSA are colored in orange. The ACE2 binding site is outlined with dotted lines.