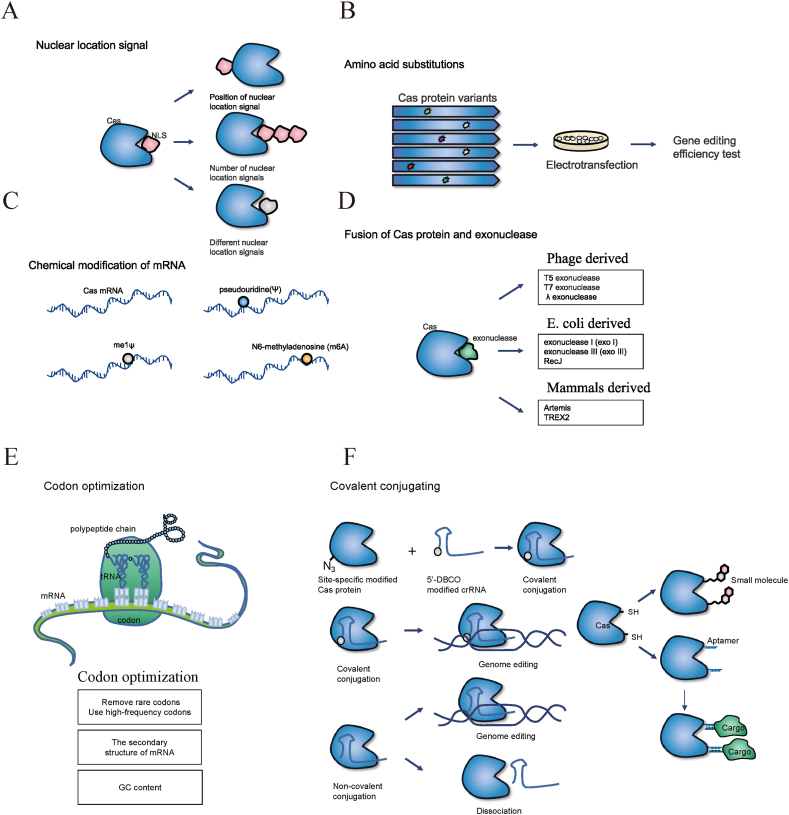
Fig. 4.
Cas-related typical operations that can improve editing efficiency. (A) Influence of NLS on editing efficiency. Factors that affect the accessibility of Cas protein to the genome include the location (N- or C-terminal), number, and type of NLS. (B) Effect of amino acid substitution in Cas protein on editing efficiency. The Cas protein variant library is generated by engineering the Cas protein, and then transfected into the cell. The editing efficiency is tested to find the Cas variant with significantly improved efficiency. (C) Effect of chemical modification of Cas mRNA on editing efficiency. Chemical modification of Cas mRNA can affect mRNA stability. Representative chemical modifications of Cas mRNA include pseudouridine (Ψ), me1ψ, and N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification. (D) Fusion of Cas protein with exonuclease. Exonucleases can be fused to the Cas nuclease to increase incompatible overhangs. Exonucleases are generally classified according to their source. (E) Cas protein codon optimization. Codon optimization of the Cas protein coding sequence for the host is beneficial to Cas protein expression. (F) Covalent conjugation of Cas protein. Cas protein and crRNA covalent conjugation can ensure that ribonucleoprotein will not dissociate before reaching the target site, thus improving efficiency. An adapter can be added to the Cas protein to allow conjugation of other molecules. Cas: CRISPR-associated proteins; NLS: nuclear localization signal.