FIGURE 1.
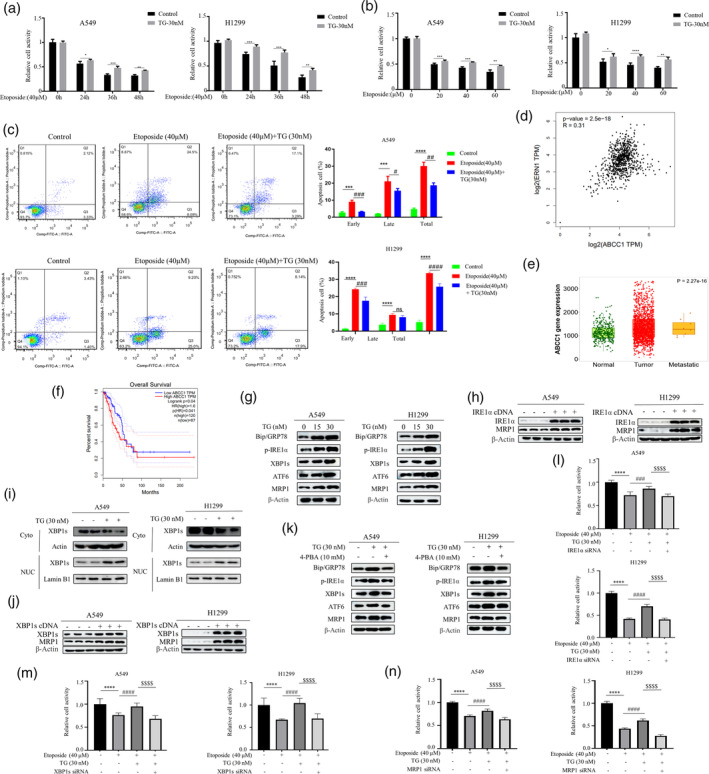
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Orchestrates Chemotherapy Resistance Through the IRE1α‐XBP1‐MRP1 Axis. (a) The A549 and H1299 cells were treated with etoposide (40 μM) for different time point (left panel) and various concentrations (right panel) in the presence or absence of TG (30 nM). MTT assay was used to detect cell viability (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 for difference from control cells). (b) The A549 and H1299 cells were pretreated with TG (30 nM) for 2 h and then were treated with etoposide (20, 40, and 60 μM) for 48 h. Cell viability was assessed using the MTT assay. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 for difference from control cells). (c) H1299 and A549 cells were treated with etoposide (40 μM) in the presence or absence of TG (30 nM). Flow cytometry analysis revealed that TG could induce resistance to etoposide in NSCLC. The bars represent the mean ± S.D. of triplicates (***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 for difference from control cells, # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001, #### p < 0.0001 for difference from etoposide‐treated cells by ANOVA with Dunnett's correction for multiple comparisons, ns means no statistical difference). (d) The correlation between ABCC1 with UPR related gene ERN1 (IRE1) expression from GEPIA data (GEPIA‐LUAD). (e) The results of the TCGA database statistical analysis reveal that the MRP1 protein encoded by ABCC1 is highly expressed in cancer cells. (f) The results of the GEPIA database reveal a correlation between the expression of MRP1 and the prognosis of lung cancer cell. (g) Western blot revealed that treating H1299 and A549 cells with TG (15, 30 nM) for 48 h resulted in a dose‐dependent enhancement of MRP1 protein expression. (h) The cells were transfected with IRE1α and XBP1s cDNA for 48 h. Western blot analysis demonstrated an increase in the expression level of MRP1 upon overexpression of IRE1α and XBP1s. (i) Cells treated with TG (30 nM) for 12 h or untreated subjected to subcellular fractionation. Equivalent celly lysates from cytoplasmic and nuclear fraction were analyzed by Western blot for subcellular localization of XBP1s. (j) After transfecting cells with XBP1s cDNA, Western blot analysis revealed the expression level of XBP1s and MRP1. (k) Western blot analyzed the expression levels of Bip/GRP78, phosphorylated IRE1α, XBP1s, ATF6, and MRP1 after treatment A549 and H1299 cells with 4‐PBA (10 mM) in the presence or absence of TG (30 nM). (l–n) The A549 and H1299 cells were first transfected with siRNA of IRE1α, XBP1s or MRP1. At 48 h post‐transfection, cells were treated with etoposide for 24 h in the presence and absence of TG followed by MTT assay (****p < 0.001 for difference from control cells, #### p < 0.0001 for the difference from etoposide‐treated cells, $$$$ p < 0.001 for difference from etoposide and TG‐treated cells by ANOVA with Dunnett's correction for multiple comparisons).
