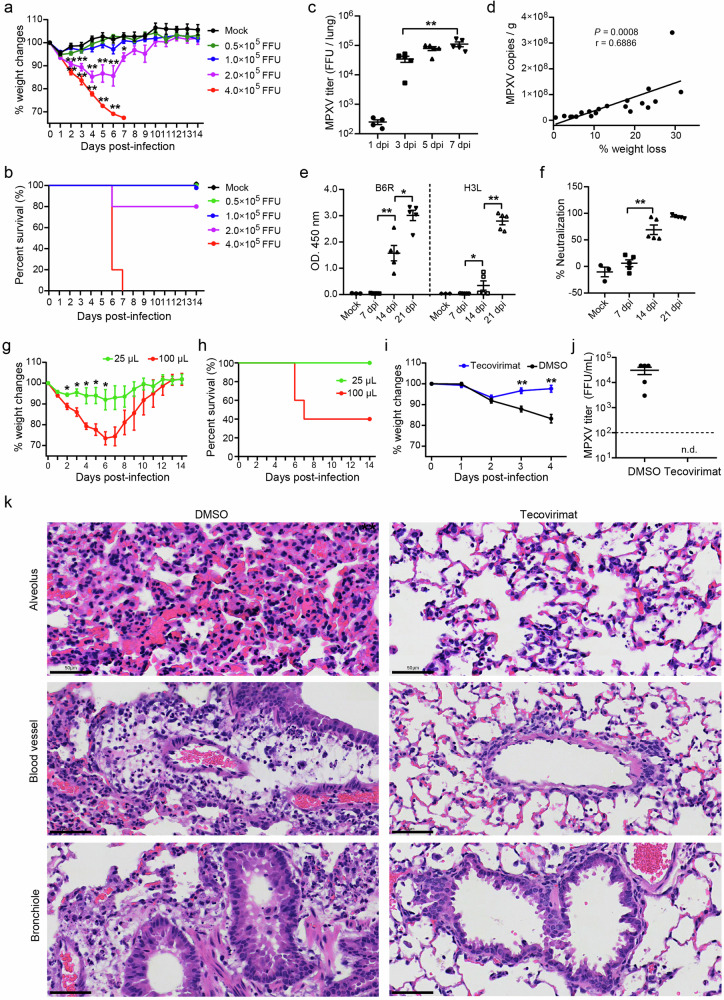
Fig. 1. Pathogenic infection model of MPXV/SZTH42 in BALB/c mice for antiviral drugs evaluation.
a–c Groups of 6- to 8-week-old female BALB/c mice were infected intranasally with doses of MPXV/SZTH42 between 0.5 × 105 and 4 × 105 FFU in total volume of 50 μL (n = 5). Control mice were mock infected with virus diluent (n = 3). Animals were monitored for weight loss (a) and death (b) for 14 days post-infection. Infectious virions in the lungs of mice infected with 4 × 105 FFU were titrated at indicated time points (c). d Mice were intranasally infected with 3 × 105 FFU under mild anesthesia (n = 20). The correlation between the percentage of weight loss and lung viral loads determined by qPCR was analyzed at 4 dpi. e, f Groups of mice were intranasally infected with 3 × 105 FFU (n = 5) or virus dilute (Mock, n = 3). Levels of B6R- and H3L-specific antibodies (e) and serum neutralizing activity (f) were determined by ELISA and Focus Reduction Neutralization Test (FRNT), respectively. g, h Groups of mice were intranasally infected with 2 × 105 FFU in total volume of 25 μL or 100 μL (n = 5). Animals were monitored for weight loss (g) and death (h) for 14 days post-infection. i–k Mice were infected with 4 × 105 FFU and treated via oral gavage from the challenge day with tecovirimat (10 mg/kg) or DMSO daily for 4 consecutive days (n = 5). Weight changes were monitored for 4 days (i), and infectious MPXV titers in lungs at 4 dpi were determined by focus-forming assay (j). The dashed line represents the limit of detection of the assay. n.d., not detected. Representative images of hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining of lung tissue sections at 4 dpi (k). Scale bars, 50 μm. Error bars indicate SEM (a, c, e–g, i, j). Statistical significance was evaluated using Student’s t-test (a, c, e–g, i). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.