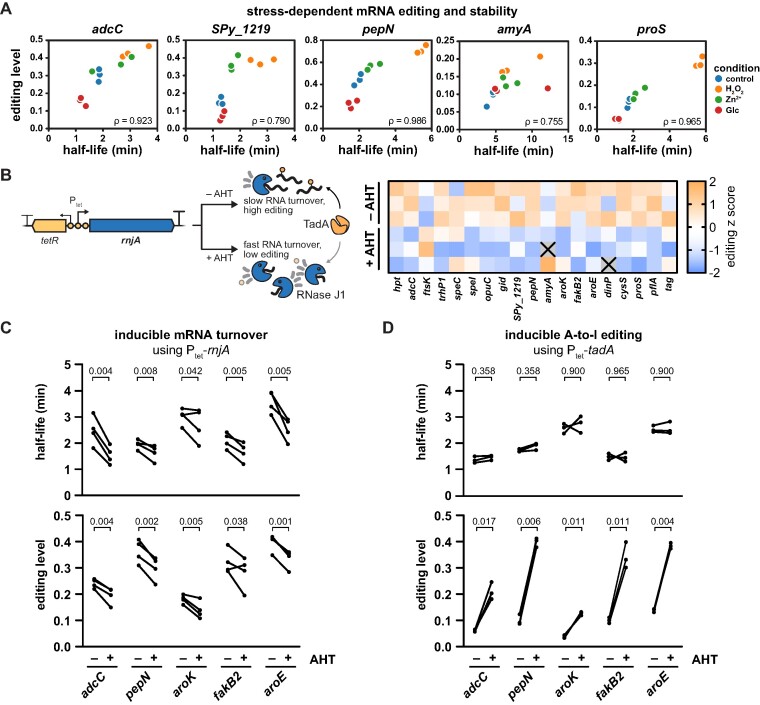
Figure 7.
Changes in mRNA stability cause A-to-I editing dynamics. (A) Correlation of A-to-I editing and mRNA half-life in response to H2O2, zinc and glucose. S. pyogenes SF370 was exposed to 1.0 mM H2O2, 0.5 mM ZnSO4 or 0.5% (w/v) glucose at mid-logarithmic phase for 30 min, and rifampicin was added to determine half-lives by qRT-PCR. Half-lives, editing levels and Spearman's ρ are shown. (B)S. pyogenes Ptet-rnjA, harbouring the AHT-inducible Ptet promoter to control the expression of the RNase J1-encoding rnjA, was grown in the presence or absence of 0.1 ng/ml AHT in THY to mid-logarithmic growth phase, and A-to-I editing was analysed by RNA sequencing. Absolute editing levels were transformed to editing z scores and are shown as a heatmap. (C)S. pyogenes Ptet-rnjA was grown in the presence or absence of 0.1 ng/ml AHT in C medium to mid-logarithmic growth phase and treated with rifampicin. Editing levels and mRNA half-lives were analysed as described in (A), and paired replicate values are shown by lines. (D) Rifampicin assay and editing analysis were performed as in (C), but with S. pyogenes Ptet-tadA grown in the presence or absence of 100 ng/ml AHT. (C, D) Statistical analysis was performed using paired t-tests, and P-values were adjusted for a false discovery rate of 5% using the procedure of Benjamini, Krieger and Yekutieli.