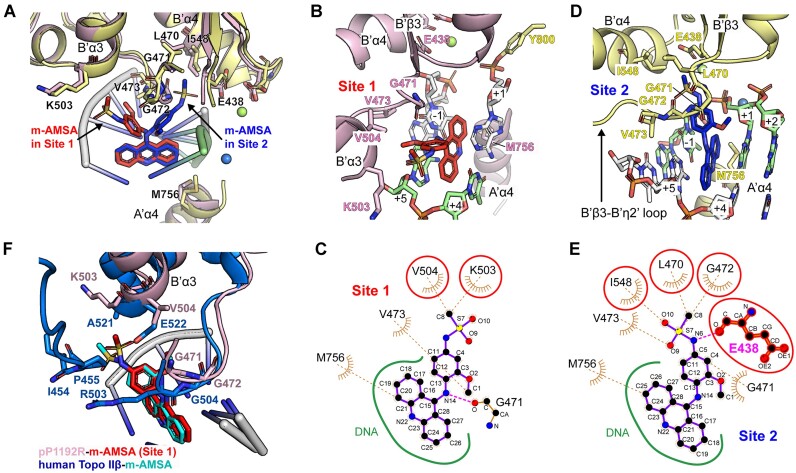
Figure 5.
Structural basis for dual modes of pP1192R inhibition by m-AMSA. (A) Structural superimposition of Site 1 and Site 2. The two protomers are pink and yellow, with m-AMSA red in Site 1 and blue in Site 2. The key residues involved in m-AMSA–pP1192R interaction are shown as sticks. (B and D) Detailed view of drug-protein interaction at Site 1 (B) and Site 2 (D). Key residues involved in m-AMSA-pP1192R interaction are shown and labelled. Mg2+ ions are depicted as spheres. (C and E) LigPlot analysis of drug-protein interaction at Site 1 (C) and Site 2 (E). The residue E438, which is involved in hydrogen bonding, is shown as a sphere and a stick, and the amino acids that differ at the two interaction sites are circled in red. (F) Structural superimposition of m-AMSA-binding sites in human Topo IIβ (PDB code: 4G0U) and pP1192R (Site 1).