Extended Data Fig. 1. Action of EVN is gene specific and does not involve an obligatory translation initiation arrest.
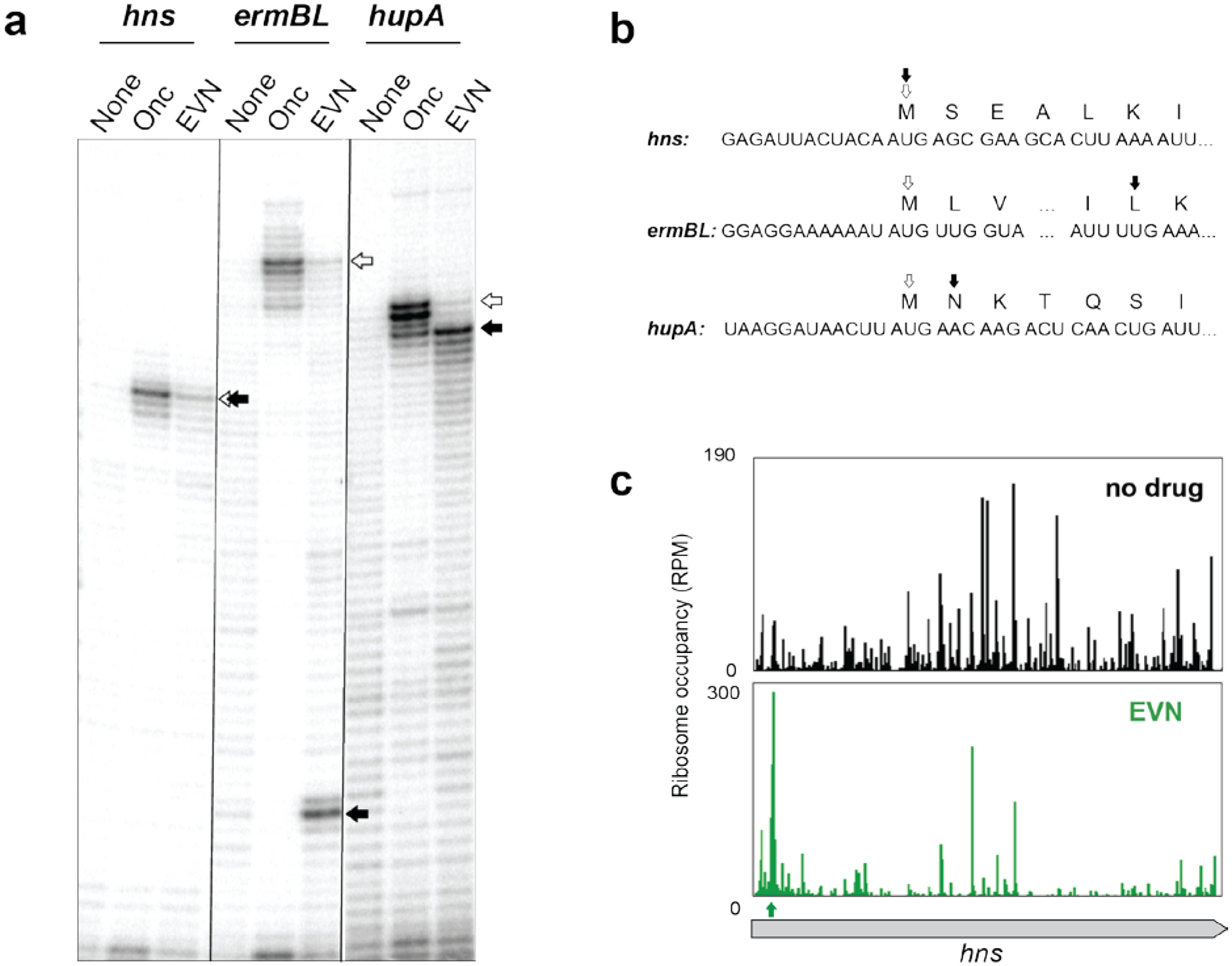
a, In vitro toeprinting experiments to analyze EVN-dependent translation arrest. Selection of the model genes was based on the results of Ribo-seq analysis (hupA) or those tested in previous reports (hns and ermBL)7,13. Open arrows indicate toeprint bands representing ribosomes stalled at the start codons by the action of initiation inhibitor oncocin (Onc)21. Black arrows point to the bands representing EVN-stalled ribosomes. Shown is a representative gel from at least two independent experiments. b, The nucleotide sequences of the relevant portions of the mRNA templates used in the toeprinting experiments shown in (a) and amino acid sequences of the encoded proteins. The open and filled arrows are as in (a). c, Ribosome profiling does not show any pronounced EVN-induced ribosome stalling at the hns start codon in E. coli cells. The first strong drug-induced translation arrest (green arrow) occurs at the codon 5 of hns.
