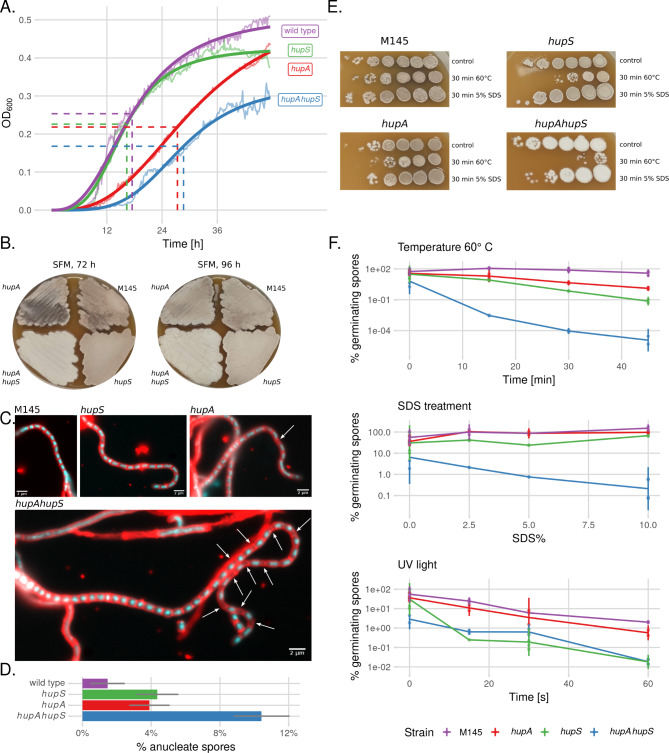
Fig. 1.
Deletion hupA or/and hupS inhibits growth and increases stress sensitivity of S. coelicolor spores A. Growth curves of wild type (purple), ΔhupA (red), ΔhupS (green) and ΔhupAΔhupS (blue) s trains in liquid ‘79’ medium. Bold lines represent logistic model while striped lines show calculated half time calculated. B. Colonies of wild type, ΔhupA, ΔhupS and ΔhupAΔhupS s trains on solid SFM medium after incubation in 30 °C for 72 and 96 h. Grey appearance of colonies indicates sporulation. C. Microscopic images of wild type, ΔhupA, ΔhupS and ΔhupAΔhupS hyphae stained with DAPI (blue, DNA) and WGA-Texas Red (red, cell wall). White arrows indicate positions of anucleate prespore compartments. Scale bar 2 μm. D. Percentage of anucleate spores in sporulating hyphae of wild type (purple, 547 spores), ΔhupA (red, 1051 spores), ΔhupS (green, 1077 spores) and ΔhupAΔhupS (blue, 1344 spores) s trains. Grey lines represent 95% confidence interval. E. Growth of wild type, ΔhupA, ΔhupS and ΔhupAΔhupS s trains after exposure of spores to high temperature (60 °C) or detergent (5% SDS) for 30 min before plating. Serial dilutions of all strains were plated on solid SFM medium. F. Percentage of germinating spores of wild type (purple), ΔhupA (red), ΔhupS (green) and ΔhupAΔhupS (blue) s trains after exposure to high temperature (60 °C), detergent (5% SDS) or UV light. Lines show mean values while errorbars represent standard deviation