Figure 10: Diagram of a theoretical renal aldosterone-endothelin feedback system (RAEFS) in the collecting duct.
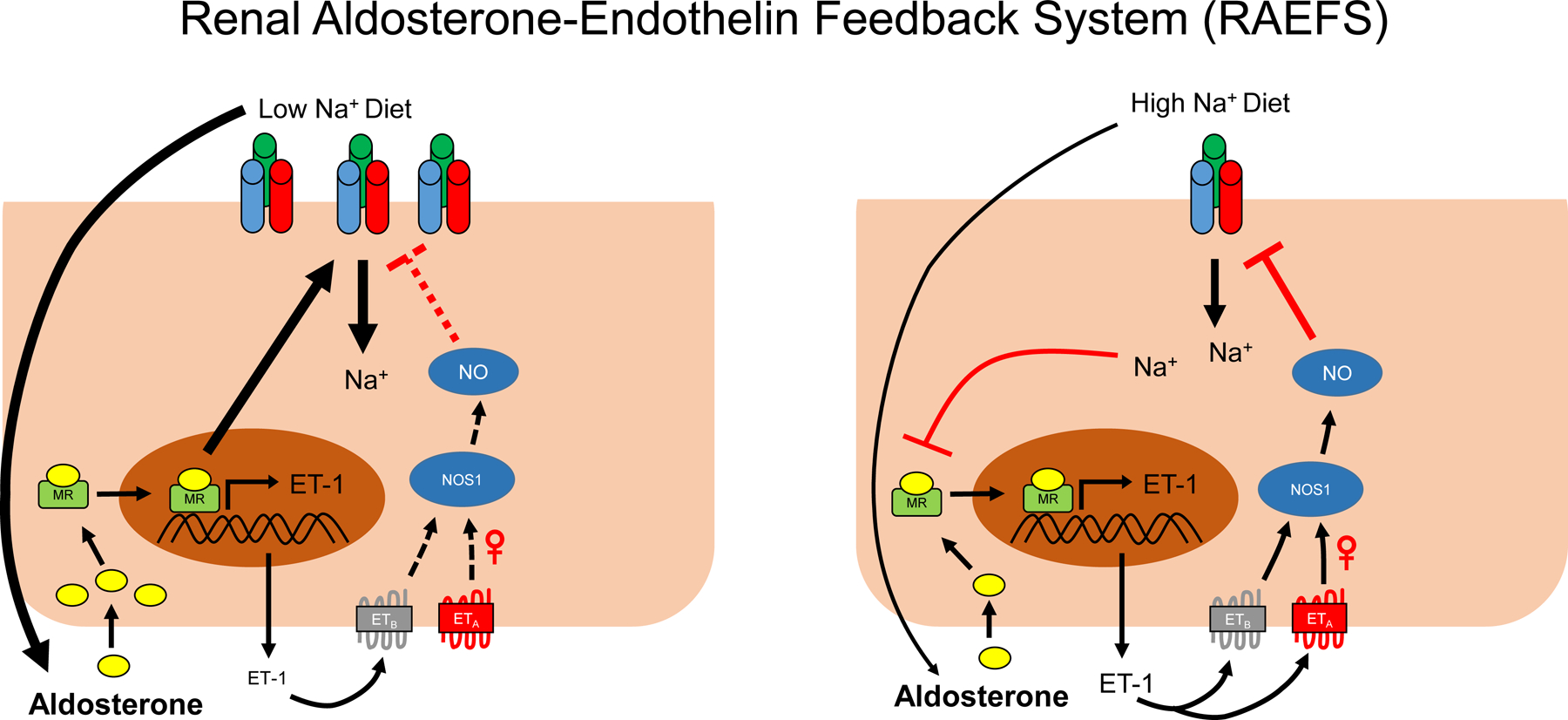
In response to a low Na+ intake, high aldosterone levels activate mineralocorticoid receptors (MR), but the production of endothelin-1 (ET-1) is attenuated by reduced distal luminal Na+ delivery and flow. Consequently, ET-1 mediated inhibition of ENaC in the collecting duct (CD) is reduced and the CD is poised to enhance Na+ absorption. When aldosterone is inappropriately high for the dietary Na+ content, high luminal Na and flow serve to enhance aldosterone mediated ET-1 activity which reduces Na absorption. Evidence for a sex-dependent natriuretic effect of ET-1 via endothelin A (ETA) receptors has been shown previously by Nakano et al (565). Dashed line indicates attenuation of pathway. UNaV, urinary sodium excretion; ETB, endothelin B receptors; NOS1, nitric oxide synthase 1; NO, nitric oxide.
