Figure 12: Molecular pathways through which aldosterone can stimulate ENaC.
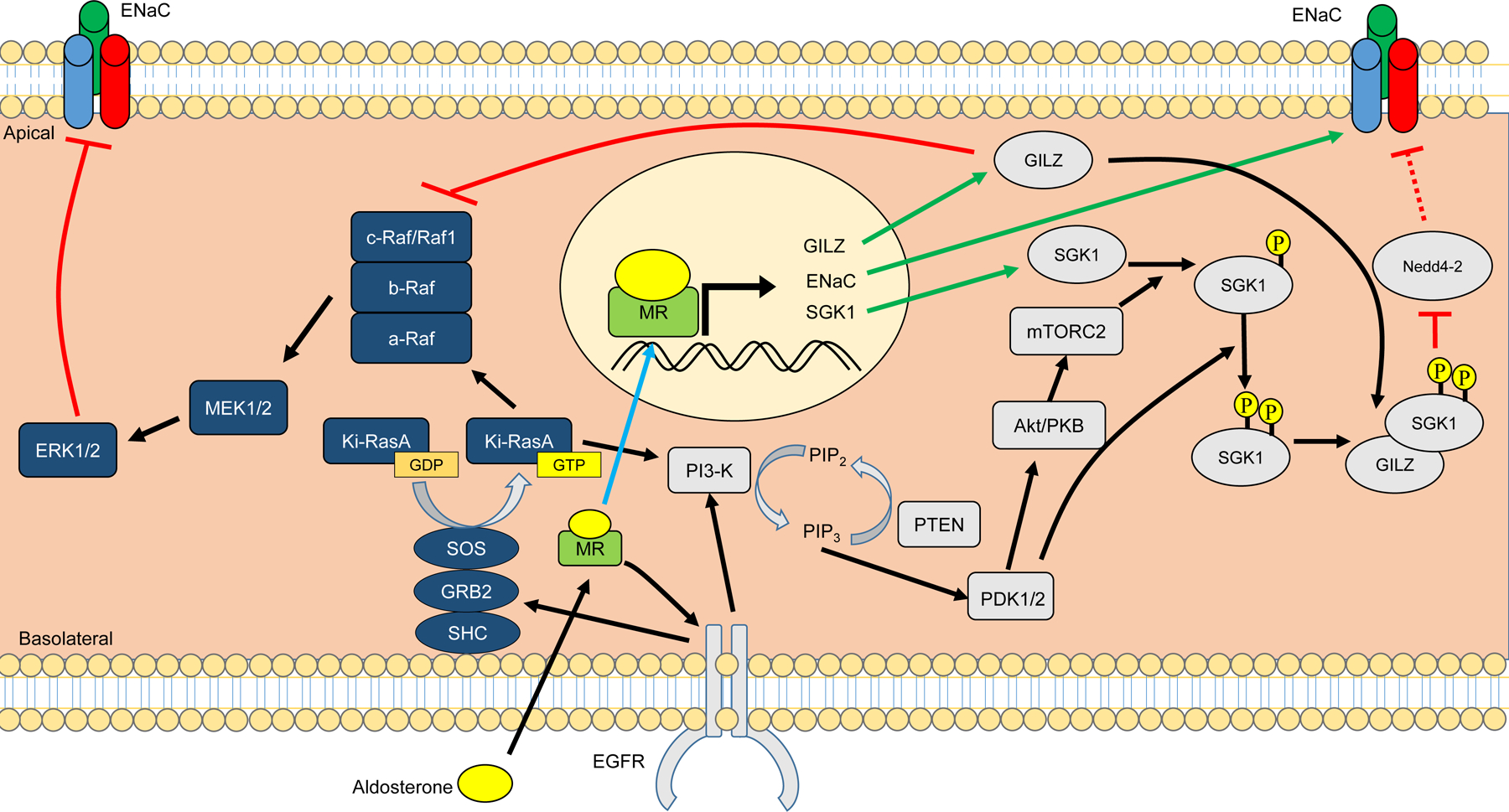
Mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) activation by aldosterone leads to stimulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Stimulation of EGFR lead to multiple cascading pathways, including the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K) pathways. The MAPK pathway leads to an inhibition of ENaC by the ERK1/2, reducing Na+ reabsorption and promoting urinary Na+ excretion. The PI3-K pathway leads to the stimulation of ENaC through the synergistic inhibition of the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-2 by MR transcription products SGK1 and GILZ. GILZ can also inhibit the ability of the MAPK pathway to inhibit ENaC by inhibiting Raf1 (c-Raf). Black arrows indicate direction of pathways. Blue arrows indicate aldosterone-bound MR relocating to the nucleus. Green arrows indicate MR transcription products. ENaC, epithelial sodium channel; GILZ, glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper; SGK1, serum- and glucocorticoid-induced kinase 1; PKB, protein kinase B (also known as Akt), PTEN, Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase; mTORC2, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2, PDK1/2, phosphoinositide-dependent kinases 1 and 2; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2; MEK, MAPK/ERK kinase or mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MAPKK).
