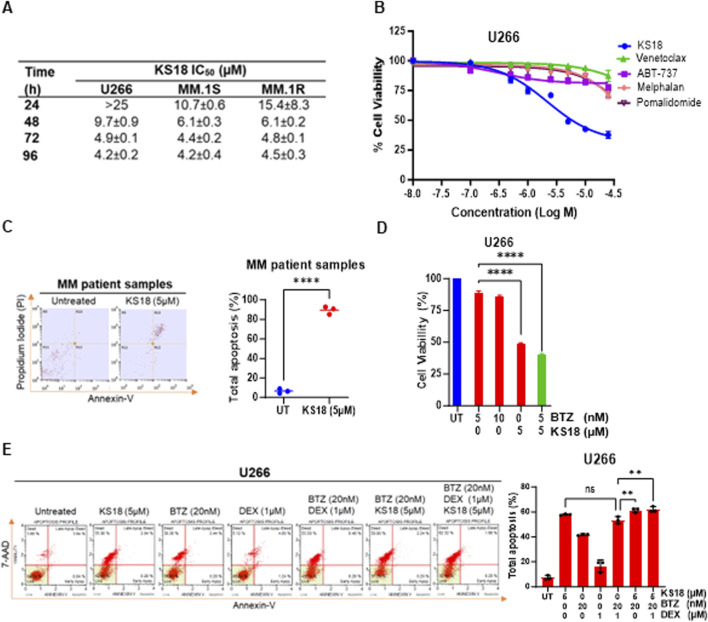
FIGURE 4.
KS18 is effective against MM cells, synergize with bortezomib and causes apoptosis in MM patients. (A), A panel of human MM cell lines (U266, MM.1S, and MM.1R) were treated with increasing doses of KS18 (0–25 μM) for 24, 48, 72, and 96 h, and the cytotoxicity of KS18 was determined using the MTT assay. The IC50 values were calculated using GraphPad prism. (B), U266 cells were subjected to escalating concentrations (0–25 μM) of KS18 and several chemotherapeutic agents (venetoclax, ABT-737, melphalan, and pomalidomide) for 72 h, after which cell viability was evaluated using the MTT assay. (C), MM patient samples (n = 3) were subjected to treatment with or without KS18 (5 µM) for a duration of 24 h. The Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Assay was conducted via FACS. The percentage of total apoptosis was calculated as [(% cell death in treated cells − % cell death in control)/(% viable cells in control) × 100]. (D), U266 cells were subjected to a 72-h treatment with bortezomib (BTZ) at concentrations of 5 and 10 nM, either alone or in conjunction with KS18 at 5 μM, and cell viability was assessed using the MTT test. (E), U266 cells were subjected to a 24-h treatment with KS18 (5 µM) either alone or in conjunction with BTZ (20 nM) and dexamethasone (DEX) (1 µM), thereafter stained with Annexin V dye and evaluated by the Muse® Cell Analyzer. The total count of apoptotic cells was quantified for samples (n = 3), and one-way ANOVA was conducted utilizing GraphPad Prism software. In all experiments cells treated with vehicle served as the control group. GraphPad Prism was utilized to generate graphs and statistical analysis. ****P ≤ 0.0001, **P < 0.01, ns, not significant.