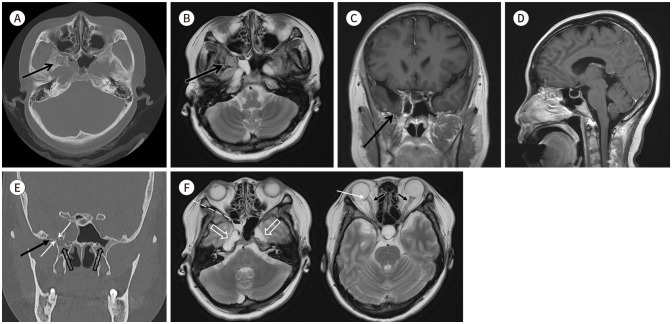
Fig. 1. Spontaneous lateral sphenoid cephalocele in a 39-year-old female patient, presenting radiologic features indicative of intracranial hypertension.
A. Axial brain CT image in the bone window shows a multilobulated shaped bony erosion (arrow) in the greater wing of the right sphenoid bone.
B. T2-weighted axial brain MRI shows an isodense lesion (arrow) with brain parenchyma within the space. The lesion also shows continuity with the adjacent temporal lobe parenchyma.
C. T1 enhanced coronal brain MRI shows a lesion (arrow) contiguous with the adjacent temporal lobe parenchyma.
D. T1 enhanced sagittal brain MRI shows sella turcica widening and a partially empty sella.
E. Coronal bone algorithm CT demonstrating pneumatization of bilateral sphenoid sinuses extending to the lateral recess, the right side of which is opacified with CSF (empty arrows). Additionally, it reveals a bony defect (white arrows), which communicates between the lateral recess of the right sphenoid sinus and the arachnoid pit (black arrow).
F. T2 axial brain MRI (left) shows the air-fluid level in the right sphenoid sinus (dashed line) and bilateral widening of Meckel’s cave (open arrows). T2 axial brain MRI (right) shows a small amount of CSF accumulation within the bilateral optic nerve sheaths (black arrows) and sclera flattening of the right posterior globe (white arrow).
CSF = cerebrospinal fluid