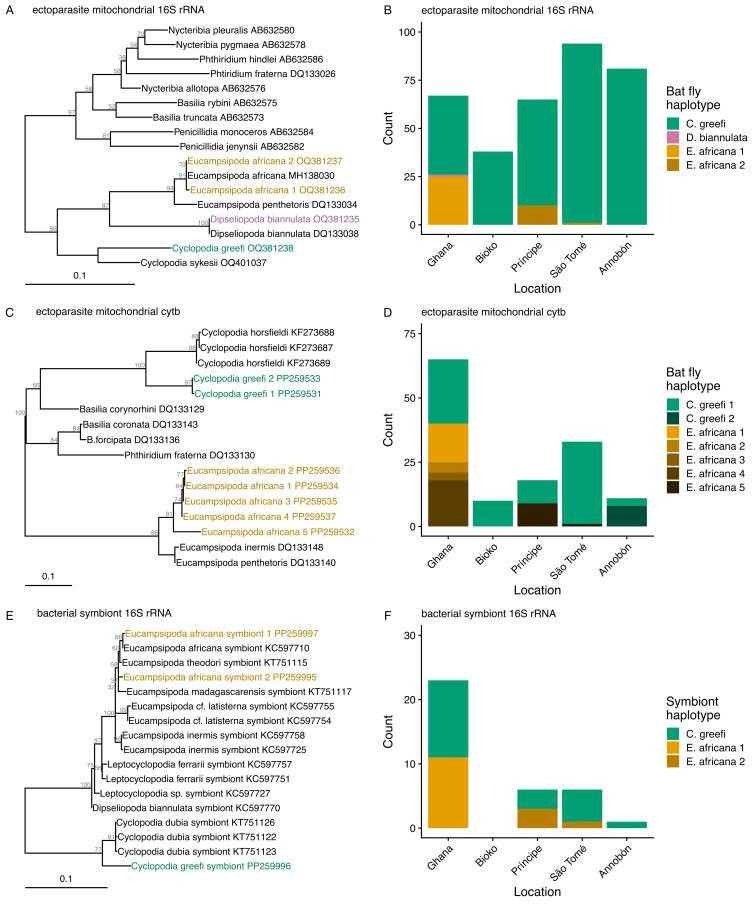
Figure 3.
Haplotyping of bat fly species and Enterobacterales symbionts. Bat fly species were identified by sequencing 375 bp of mitochondrial 16S rRNA (A) and 387 bp of cytb (C) while bacterial symbionts of flies were identified by sequencing 575 bp of bacterial 16S rRNA (E). Maximum likelihood trees were generated in IQ-Tree using the appropriate substitution models based on BIC (TIM2 + F + G4 for ectoparasite mitochondrial 16S rRNA, TIM + F + G4 for cytb, K2P + R2 for bacterial symbiont 16S rRNA). Nodal support (shown in grey next to branches) was estimated from 1000 bootstrap iterations. GenBank accession numbers are given next to published reference sequences. Observed counts of haplotypes across locations (B, D and F) are shown based on the total number of specimens haplotyped at each marker. In all panels, the colours indicate separate bat fly species and symbionts: Cyclopodia greefi (green), Eucampsipoda africana (orange) and Dipseliopoda biannulata (pink).