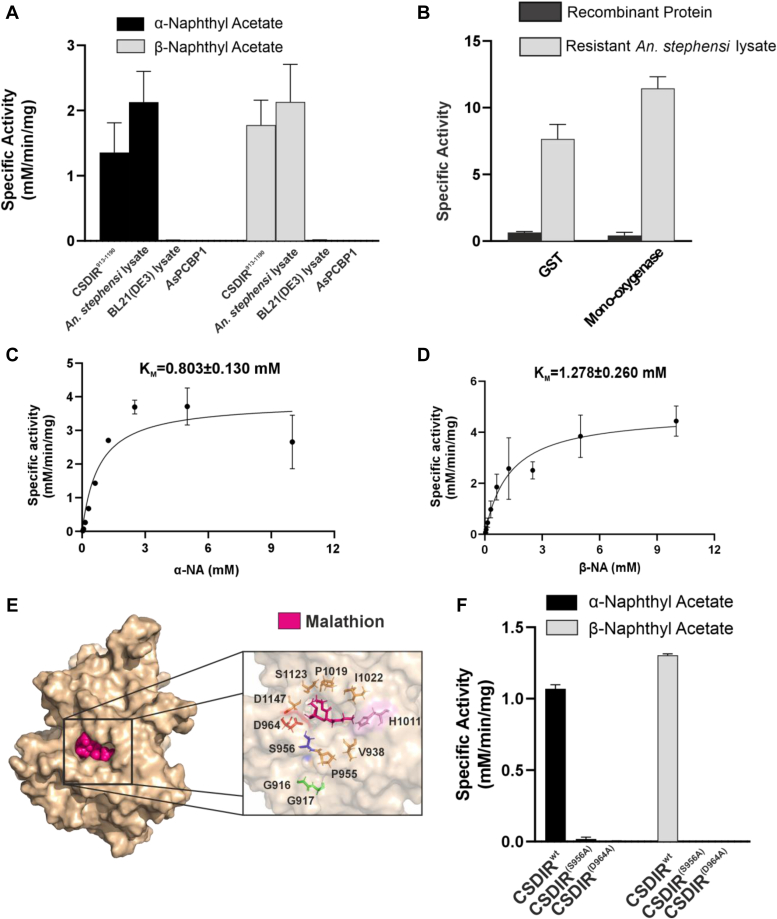
Figure 6.
Recombinant CSDIR913-1190showed esterase-like activity.A, the bar graph showing the specific activity of recombinant CSDIR913-1190 against α-naphthyl acetate and β-naphthyl acetate compared with resistant female An. stephensi lysate. BL21(DE3) lysate and AsPCBP1 served as a negative control. B, the bar graph showing the specific activity of recombinant CSDIR913-1190 against GST and Mono-oxygenase compared with resistant female An. stephensi lysate. C, a graph indicating the binding kinetics of recombinant CSDIR913-1190 with α-naphthyl acetate, Km was calculated using non-linear Michaelis-Menten regression. D, a graph indicating the binding kinetics of recombinant CSDIR913-1190 with β-naphthyl acetate, Km was calculated using non-linear Michaelis-Menten regression. E, CSDIR913-1190 3D model showing putative binding pocket. Malathion (as a reference) inside the binding pocket is highlighted in magenta color. Residues S956 (blue), D964(Red), and H1011 (Pink) form the catalytic triad whereas G916 and G917 (green) form the oxyanion hole. F, a bar graph showing the specific activity of recombinant CSDIR913-1190(CSDIRwt) and CSDIR mutants (CSDIR(S956A), CSDIR(D964)) against α-naphthyl acetate and β-naphthyl acetate.