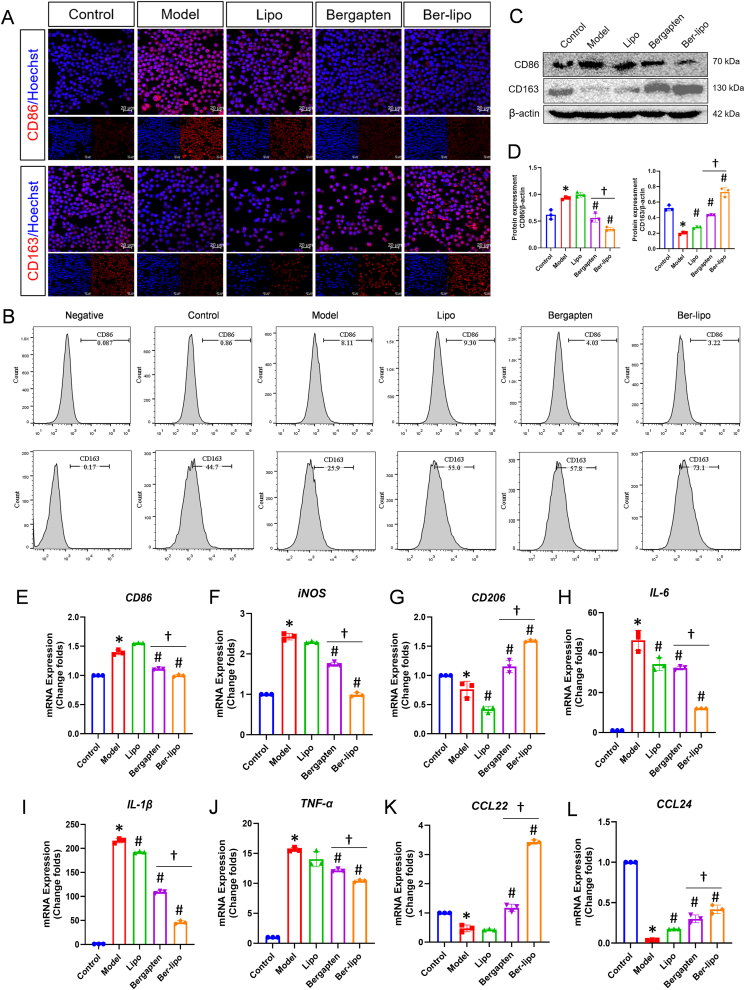
Fig. 3.
Ber-lipo's effects on maintaining balance between M1 and M2 macrophage polarization in vitro. (A) The distribution of CD86-marked M1 and CD163-indicated M2 in RAW264.7 cells by immunofluorescent staining (red). Images were captured using 40 × oil immersion lens of confocal microscope. Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) The proportion of CD86+ M1 and CD163+ M2 in RAW264.7 cells by flow cytometry. (C) Protein expression of CD86 and CD163 in RAW264.7 cells by Western blot. (D) Quantification of protein bands by imageJ software (n = 3). (E–L) The normalized mRNA expressions of CD86, iNOS, CD206, IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, CCL22, and CCL24 using qRT-PCR. Internal control, α-Tubulin. M1 phenotypic markers: CD86, iNOS, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α. M2 phenotypic markers: CD163, CD206, CCL22, and CCL24. Model, RAW264.7 cells challenged by 100 ng/ml LPS. ∗P < 0.05 vs Control. #P < 0.05 vs Model. †P < 0.05.