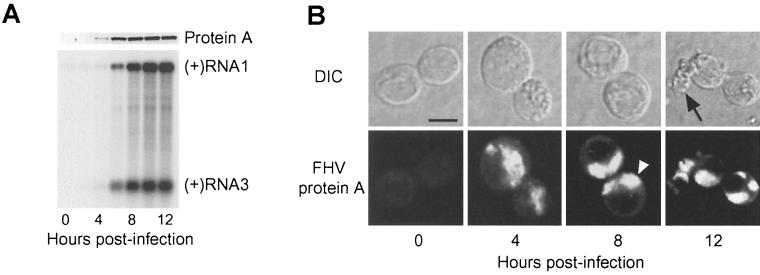
FIG. 2.
FHV protein A expression correlates with genomic RNA1 replication and subgenomic RNA3 synthesis, and protein A localizes to discrete intracellular structures in infected Drosophila DL-1 cells. (A) Temporal pattern of protein A expression and FHV RNA replication. Total protein from an equivalent number of cells per sample was separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and immunoblotted with rabbit anti-protein A (upper blot). Total-protein staining showed equivalent protein loading in all lanes (data not shown). One microgram of total RNA per sample was separated on denaturing formaldehyde-agarose gels, transferred to a nylon membrane, and blotted with a 32P-labeled complementary riboprobe that detected positive-strand RNA1 and RNA3 (lower blot). The positions of RNA1 and RNA3 are indicated on the right. (B) Temporal pattern of protein A localization. FHV-infected cells were incubated on polyethyleneimine-coated chamber slides, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100, and immunostained with rabbit anti-protein A, followed by TR-labeled secondary antibodies. DIC and confocal immunofluorescence images of the same cells are shown for each indicated time postinfection. The open arrowhead in the 8-h time point immunofluorescence image indicates the clustering and polarization of protein A in infected cells, and the closed arrow in the 12-h time point DIC image indicates a degenerating cell, characteristic of FHV-induced cytopathic effects (57). Bar = 5 μm.