FIGURE 1.
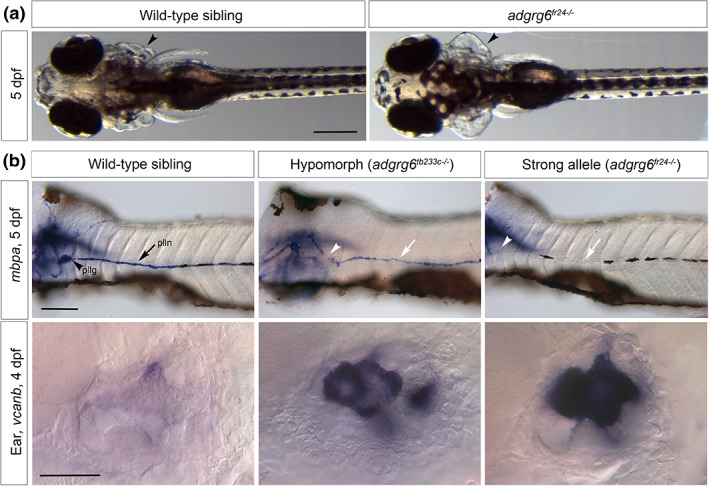
Otic and myelination phenotypes in zebrafish adgrg6 mutants. (a) Phenotypically wild‐type sibling (left panel, ventral view) and homozygous adgrg6 fr24−/− mutant (right panel, dorsal view), showing swollen otic vesicles (arrowhead). Anterior to the left. Note that head and eye size, pectoral fins, pigmentation, and swim bladder inflation are all normal in the mutant. Scale bar, 200 μm. Images reproduced from Geng et al., 2013. (b) In situ hybridization to myelin basic protein a (mbpa) transcripts in the trunk (top row) and to versican b (vcanb) in the ear (bottom row). Lateral views; anterior to the left. Top row: expression of mbpa in Schwann cells of the posterior lateral line ganglion (pllg, arrowhead) and posterior lateral line nerve (plln, arrow) is reduced in the hypomorphic tb233c allele, and lost altogether in the strong fr24 allele. The blurred stain to the left in each image is expression in the central nervous system, which is unaffected in the mutants. Scale bar, 100 μm. Images reproduced from Geng et al., 2013. Bottom row: strong expression of vcanb in the ear persists abnormally in adgrg6 mutants. Scale bar, 50 μm. dpf, days post fertilization. Images reproduced from Diamantopoulou et al., 2019
